research
_and_Professor_Inkyu_Park_(right)_2.jpg)
< Ph.D. Candidate Jimin Gu (left) and Professor Inkyu Park (right) >
KAIST researchers have developed a novel wearable strain sensor based on the modulation of optical transmittance of a carbon nanotube (CNT)-embedded elastomer. The sensor is capable of sensitive, stable, and continuous measurement of physical signals. This technology, featured in the March 4th issue of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces as a front cover article, shows great potential for the detection of subtle human motions and the real-time monitoring of body postures for healthcare applications.
A wearable strain sensor must have high sensitivity, flexibility, and stretchability, as well as low cost. Those used especially for health monitoring should also be tied to long-term solid performance, and be environmentally stable. Various stretchable strain sensors based on piezo-resistive and capacitive principles have been developed to meet all these requirements.
Conventional piezo-resistive strain sensors using functional nanomaterials, including CNTs as the most common example, have shown high sensitivity and great sensing performance. However, they suffer from poor long-term stability and linearity, as well as considerable signal hysteresis. As an alternative, piezo-capacitive strain sensors with better stability, lower hysteresis, and higher stretchability have been suggested. But due to the fact that piezo-capacitive strain sensors exhibit limited sensitivity and strong electromagnetic interference caused by the conductive objects in the surrounding environment, these conventional stretchable strain sensors are still facing limitations that are yet to be resolved.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering suggested that an optical-type stretchable strain sensor can be a good alternative to resolve the limitations of conventional piezo-resistive and piezo-capacitive strain sensors, because they have high stability and are less affected by environmental disturbances. The team then introduced an optical wearable strain sensor based on the light transmittance changes of a CNT-embedded elastomer, which further addresses the low sensitivity problem of conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
In order to achieve a large dynamic range for the sensor, Professor Park and his researchers chose Ecoflex as an elastomeric substrate with good mechanical durability, flexibility, and attachability on human skin, and the new optical wearable strain sensor developed by the research group actually shows a wide dynamic range of 0 to 400%.
In addition, the researchers propagated the microcracks under tensile strain within the film of multi-walled CNTs embedded in the Ecoflex substrate, changing the optical transmittance of the film. By doing so, it was possible for them to develop a wearable strain sensor having a sensitivity 10 times higher than conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
The proposed sensor has also passed the durability test with excellent results. The sensor’s response after 13,000 sets of cyclic loading was stable without any noticeable drift. This suggests that the sensor response can be used without degradation, even if the sensor is repeatedly used for a long time and in various environmental conditions.
Using the developed sensor, the research team could measure the finger bending motion and used it for robot control. They also developed a three-axes sensor array for body posture monitoring. The sensor was able to monitor human motions with small strains such as a pulse near the carotid artery and muscle movement around the mouth during pronunciation.
Professor Park said, “In this study, our group developed a new wearable strain sensor platform that overcomes many limitations of previously developed resistive, capacitive, and optical-type stretchable strain sensors. Our sensor could be widely used in a variety of fields including soft robotics, wearable electronics, electronic skin, healthcare, and even entertainment.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.

< Figure 1. The front cover image of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, Volume 12, Issue 9. >
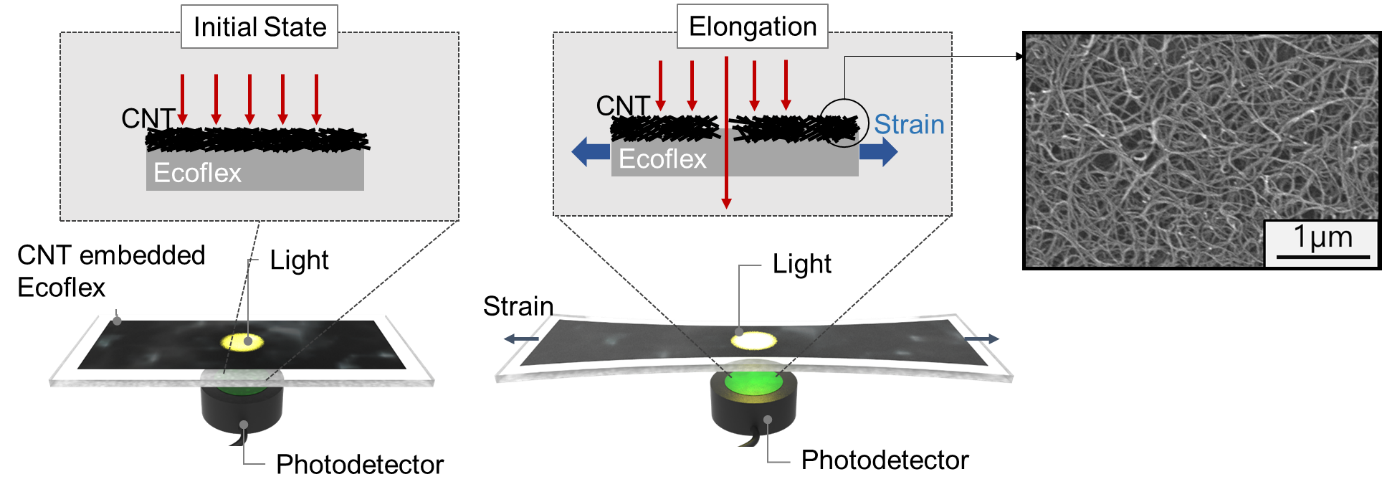
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the sensor based on the optical transmittance changes of the CNT-embedded Ecoflex thin film. >
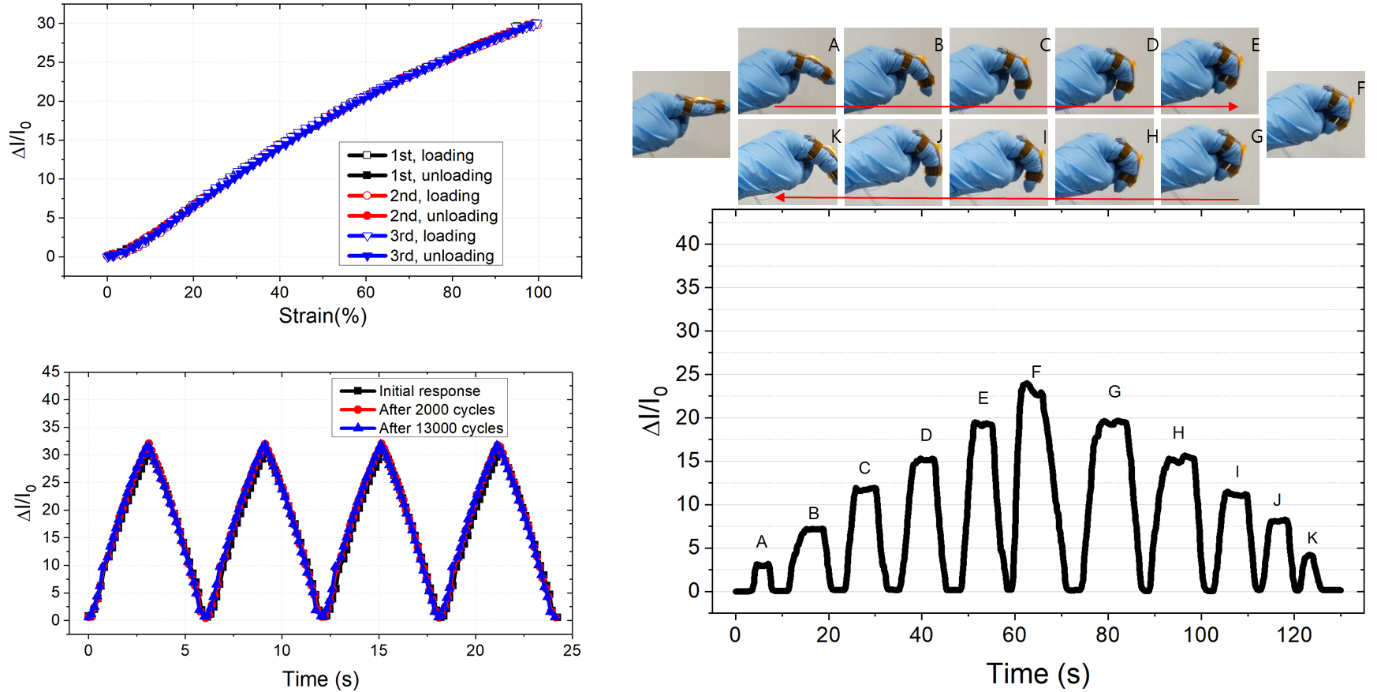
< Figure 3. High sensitivity and reliable sensing performance of the proposed sensor and its application to finger bending motion monitoring. >
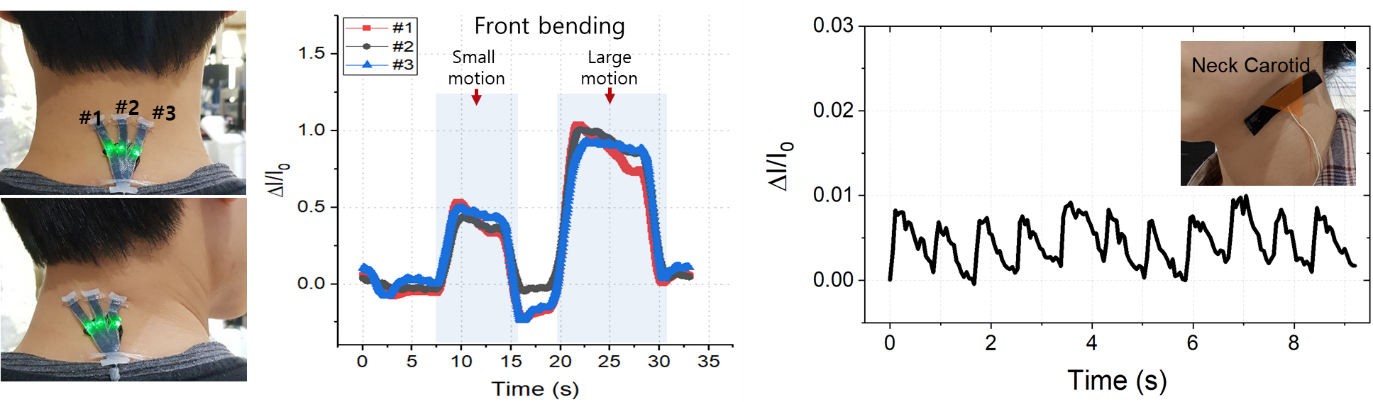
< Figure 4. Posture monitoring using 3-axes strain sensor array, and pulse monitoring on the carotid artery. >
Publication:
Jimin Gu, Donguk Kwon, Junseong Ahn, and Inkyu Park. (2020) “Wearable Strain sensors Using Light Transmittance Change of Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Elastomers with Microcracks” ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Volume 12. Issue 9. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18069
Profile:
Inkyu Park
Professor
inkyu@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
Micro/Nano Transducers Laboratory (MINT Lab)
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Profile:
Jimin Gu
Ph.D. Candidate
mint9411@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
MINT Lab
KAIST ME
(END)
-
research No More Touch Issues on Rainy Days! KAIST Develops Human-Like Tactile Sensor
Recent advancements in robotics have enabled machines to handle delicate objects like eggs with precision, thanks to highly integrated pressure sensors that provide detailed tactile feedback. However, even the most advanced robots struggle to accurately detect pressure in complex environments involving water, bending, or electromagnetic interference. A research team at KAIST has successfully developed a pressure sensor that operates stably without external interference, even on wet surfaces li
2025-03-14 -
research AI-Driven Wearable Blood Pressure Sensor for Continuous Health Monitoring – Published in Nature Reviews Cardiology
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee has proposed an innovative theoretical framework and research strategies for AI-based wearable blood pressure sensors, paving the way for continuous and non-invasive cardiovascular monitoring. Hypertension is a leading chronic disease affecting over a billion people worldwide and is a major risk factor for severe cardiovascular conditions such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure. Traditional blood pressure measurement relies o
2025-03-04 -
research KAIST Develops Wearable Carbon Dioxide Sensor to Enable Real-time Apnea Diagnosis
- Professor Seunghyup Yoo’s research team of the School of Electrical Engineering developed an ultralow-power carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor using a flexible and thin organic photodiode, and succeeded in real-time breathing monitoring by attaching it to a commercial mask - Wearable devices with features such as low power, high stability, and flexibility can be utilized for early diagnosis of various diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea < Photo 1. Fro
2025-02-13 -
research KAIST Secures Core Technology for Ultra-High-Resolution Image Sensors
A joint research team from Korea and the United States has developed next-generation, high-resolution image sensor technology with higher power efficiency and a smaller size compared to existing sensors. Notably, they have secured foundational technology for ultra-high-resolution shortwave infrared (SWIR) image sensors, an area currently dominated by Sony, paving the way for future market entry. KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of November that a research t
2024-11-22 -
research KAIST Develops Healthcare Device Tracking Chronic Diabetic Wounds
A KAIST research team has developed an effective wireless system that monitors the wound healing process by tracking the spatiotemporal temperature changes and heat transfer characteristics of damaged areas such as diabetic wounds. On the 5th of March, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the research team led by Professor Kyeongha Kwon from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, in association with Chung-Ang University professor Hanjun Ryu, developed digit
2024-03-11