research
< MS Candidate Sangjun Han (left), Dr. Seyoon Kim (center), and Professor Min Seok Jang (right) >
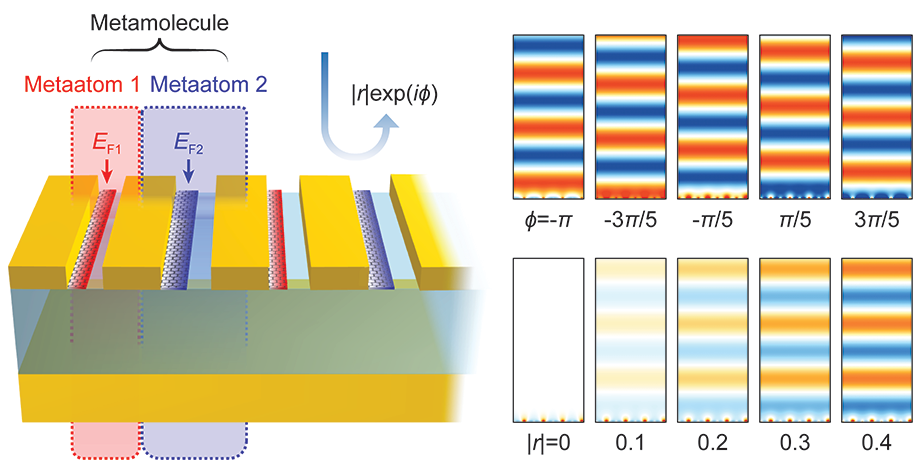
Researchers described a new strategy of designing metamolecules that incorporates two independently controllable subwavelength meta-atoms. This two-parametric control of the metamolecule secures the complete control of both amplitude and the phase of light.
A KAIST research team in collaboration with the University of Wisconsin-Madison theoretically suggested a graphene-based active metasurface capable of independent amplitude and phase control of mid-infrared light. This research gives a new insight into modulating the mid-infrared wavefront with high resolution by solving the problem of the independent control of light amplitude and phase, which has remained a long-standing challenge.
Light modulation technology is essential for developing future optical devices such as holography, high-resolution imaging, and optical communication systems. Liquid crystals and a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) have previously been utilized to modulate light. However, both methods suffer from significantly limited driving speeds and unit pixel sizes larger than the diffraction limit, which consequently prevent their integration into photonic systems.
The metasurface platform is considered a strong candidate for the next generation of light modulation technology. Metasurfaces have optical properties that natural materials cannot have, and can overcome the limitations of conventional optical systems, such as forming a high-resolution image beyond the diffraction limit. In particular, the active metasurface is regarded as a technology with a wide range of applications due to its tunable optical characteristics with an electrical signal.
However, the previous active metasurfaces suffered from the inevitable correlation between light amplitude control and phase control. This problem is caused by the modulation mechanism of conventional metasurfaces. Conventional metasurfaces have been designed such that a metaatom only has one resonance condition, but a single resonant design inherently lacks the degrees of freedom to independently control the amplitude and phase of light.
The research team made a metaunit by combining two independently controllable metaatoms, dramatically improving the modulation range of active metasurfaces. The proposed metasurface can control the amplitude and phase of the mid-infrared light independently with a resolution beyond the diffraction limit, thus allowing complete control of the optical wavefront.
The research team theoretically confirmed the performance of the proposed active metasurface and the possibility of wavefront shaping using this design method. Furthermore, they developed an analytical method that can approximate the optical properties of metasurfaces without complex electromagnetic simulations. This analytical platform proposes a more intuitive and comprehensively applicable metasurface design guideline.
The proposed technology is expected to enable accurate wavefront shaping with a much higher spatial resolution than existing wavefront shaping technologies, which will be applied to active optical systems such as mid-infrared holography, high-speed beam steering devices that can be applied for LiDAR, and variable focus infrared lenses.
Professor Min Seok Jang commented, "This study showed the independent control amplitude and phase of light, which has been a long-standing quest in light modulator technology. The development of optical devices using complex wavefront control is expected to become more active in the future."
MS candidate Sangjun Han and Dr. Seyoon Kim of the University of Wisconsin-Madison are the co-first authors of the research, which was published and selected as the front cover of the January 28 edition of ACS Nano titled “Complete complex amplitude modulation with electronically tunable graphene plasmonic metamolecules.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology.
< Schematic image of graphene plasmonic metamolecules capable of independent amplitude and phase control of light. >
< The front cover of ACS Nano published on January 28. >
Publication:
Han et al. (2020) Complete Complex Amplitude Modulation with Electronically Tunable Graphene Plasmonic Metamolecules. ACS Nano, Vol. 14, Issue 1, pp. 1166-1175. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b09277
Profile: Prof. Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://jlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Associate Professor
Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Sangjun Han
sangjun.han@kaist.ac.kr
MS Candidate
School of Electrical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
-
research KAIST Develops a Fire-risk Free Self-Powered Hydrogen Production System
KAIST researchers have developed a new hydrogen production system that overcomes the current limitations of green hydrogen production. By using a water-splitting system with an aqueous electrolyte, this system is expected to block fire risks and enable stable hydrogen production. KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd of October that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a self-powered hy
2024-10-22 -
research Atomically-Smooth Gold Crystals Help to Compress Light for Nanophotonic Applications
Highly compressed mid-infrared optical waves in a thin dielectric crystal on monocrystalline gold substrate investigated for the first time using a high-resolution scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope. KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new platform for guiding the compressed light waves in very thin van der Waals crystals. Their method to guide the mid-infrared light with minimal loss will provide a breakthrough f
2022-07-13 -
research A New Strategy for Active Metasurface Design Provides a Full 360° Phase Tunable Metasurface
The new strategy displays an unprecedented upper limit of dynamic phase modulation with no significant variations in optical amplitude An international team of researchers led by Professor Min Seok Jang of KAIST and Professor Victor W. Brar of the University of Wisconsin-Madison has demonstrated a widely applicable methodology enabling a full 360° active phase modulation for metasurfaces while maintaining significant levels of uniform light amplitude. This strategy can be fundamentally appl
2022-05-02 -
research Eco-Friendly Micro-Supercapacitors Using Fallen Leaves
Green micro-supercapacitors on a single leaf could easily be applied in wearable electronics, smart houses, and IoTs A KAIST research team has developed graphene-inorganic-hybrid micro-supercapacitors made of fallen leaves using femtosecond laser direct writing. The rapid development of wearable electronics requires breakthrough innovations in flexible energy storage devices in which micro-supercapacitors have drawn a great deal of interest due to their high power density, long lifetimes, and
2022-01-27 -
research Acoustic Graphene Plasmons Study Paves Way for Optoelectronic Applications
- The first images of mid-infrared optical waves compressed 1,000 times captured using a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope. - KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new methodology for direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon fields. This strategy will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of acoustic graphene plasmon platforms in next-generation, high-perfor
2021-03-16