research

-
research Blue-enriched White Light to Wake You Up in the Morning
(from left: Professor Hyun Jung Chung, Professor Hyeon-Jeong Suk, Taesu Kim and Professor Kyungah Choi) Here is a good news for those of who have difficulty with morning alertness. A KAIST research team proposed that a blue-enriched LED light can effectively help people overcome morning drowsiness. This study will provide the basis for major changes in future lighting strategies and thereby help create better indoor environments. Considerable research has been devoted to unmas
2019-03-06 -
research Ultrathin Digital Camera Inspired by Xenos Peckii Eyes
(Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) The visual system of Xenos peckii, an endoparasite of paper wasps, demonstrates distinct benefits for high sensitivity and high resolution, differing from the compound eyes of most insects. Taking their unique features, a KAIST team developed an ultrathin digital camera that emulates the unique eyes of Xenos peckii. The ultrathin digital camera offers a wide field of view and high resolution
2018-12-31 -
research Skin Hardness to Estimate Better Human Thermal Status
(Professor Young-Ho Cho and Researcher Sunghyun Yoon) Under the same temperature and humidity, human thermal status may vary due to individual body constitution and climatic environment. A KAIST research team previously developed a wearable sweat rate sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring. Furthering the development, this time they proposed skin hardness as an additional, independent physiological sign to estimate human thermal status more accurately. This novel approach
2018-10-17 -
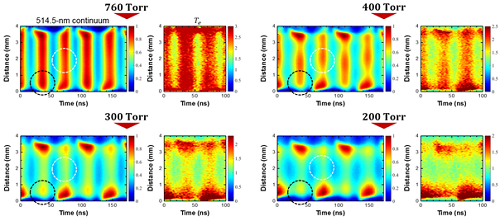
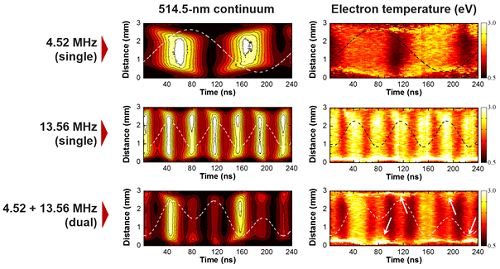
research KAIST Finds the Principle of Electric Wind in Plasma
(From left: Professor Wonho Choe and PhD Sanghoo Park) A KAIST team identified the basic principle of electric wind in plasma. This finding will contribute to developing technology in various applications of plasma, including fluid control technology. Professor Wonho Choe from the Department of Physics and his team identified the main principle of neutral gas flow in plasma, known as ‘electric wind’, in collaboration with Professor Se Youn Moon’s team at Chonbuk National Uni
2018-03-02 -
research Finding Human Thermal Comfort with a Watch-type Sweat Rate Sensor
(from left: Professor Young-Ho Cho and Researcher SungHyun Yoon) KAIST developed a watch-type sweat rate sensor. This subminiature device can detect human thermal comfort accurately and steadily by measuring an individual’s sweat rate. It is natural to sweat more in the summer and less in the winter; however, an individual’s sweat rate may vary in a given environment. Therefore, sweat can be an excellent proxy for sensing core body temperature. Conventional swe
2018-02-08