research

< Ph.D.candidate Lee, Professor Kim, and PhD candidate Kim >
A KAIST research group presented photonic capsules for injectable laser resonators using microfluidic technology. The capsule’s diameter is comparable to a human hair and stable in gas and liquid media, so it is injectable into any target volume.
The research group headed by Professor Shin-Hyun Kim in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering applied an interesting optical property from nature. Professor Kim, who has dived deep into photonic materials research inspired from nature such as the Morpho butterfly, used a trait of beetles this time.
Chrysina gloriosa, commonly known as the glorious beetle, shows a green color similar to leaves when illuminated by left-handed, circularly-polarized light while showing no color with right-handed, circularly-polarized light. This unique optical feature helps the beetles communicate with each other and protects them from predators.
The principle behind this interesting optical property of the beetles relies on helical nanostructures with left-handedness that are present on the shell of the beetles. The helical structures reflect a circularly-polarized light with the same handedness of the helix at the wavelength selected by the helical pitch through optical interference.
Such helical nanostructures can be artificially created using liquid crystals (LCs). LCs with a helical arrangement are referred to as cholesteric LCs (CLCs). The CLCs exhibit the polarization-dependent reflection of light in the same manner as the beetles and have been used for various photonic applications.
In particular, CLCs have been cast to a film format that serves as mirrorless laser resonators, unlike conventional lasing systems. However, the film-type CLCs are large in size and show unidirectional emission, which restricts the use of CLC resonators in microenvironments.
To overcome these limitations, Professor Kim’s group has encapsulated the CLCs with dual shells using microfluidic technology. The inner shell is a water layer that promotes the alignment of LC molecules and the outer shell is an elastic polymer layer that secures capsule stability and enables reversible mechanical deformation. The spherical symmetry of the capsules enables omnidirectional laser emissions. Moreover, laser intensity and lasing direction can be further controlled by deforming the capsules, while its wavelength remains tunable. This new type of CLC laser resonator is promising for laser treatments in various biomedical applications.
Professor Kim said, “The helical nanostructure used in the laser resonator resembles that of the shell of chrysina gloriosa. Humans learn from nature and engineer materials to create something unprecedented.”
This research was led by graduate student Sang Seok Lee and an article entitled “Wavelength-tunable and shape-reconfigurable photonic capsule resonators containing cholesteric liquid crystals” was published online on June 22, in Science Advances.
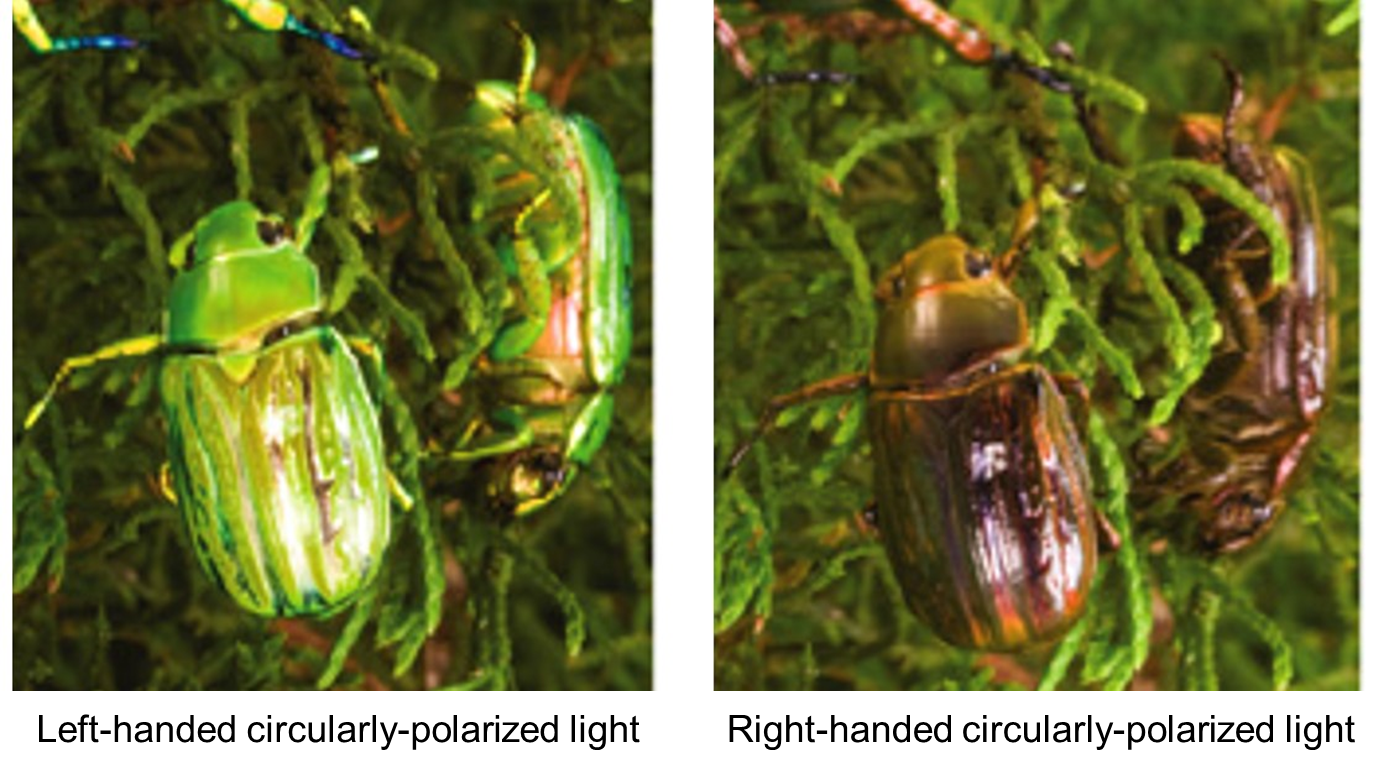

Figure 1. Chrysina gloriosa illuminated by left-handed (left panel) and right-handed (right panel) circularly-polarized lights.
(Image source: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2010.05.036 , permitted for reuse in news media)
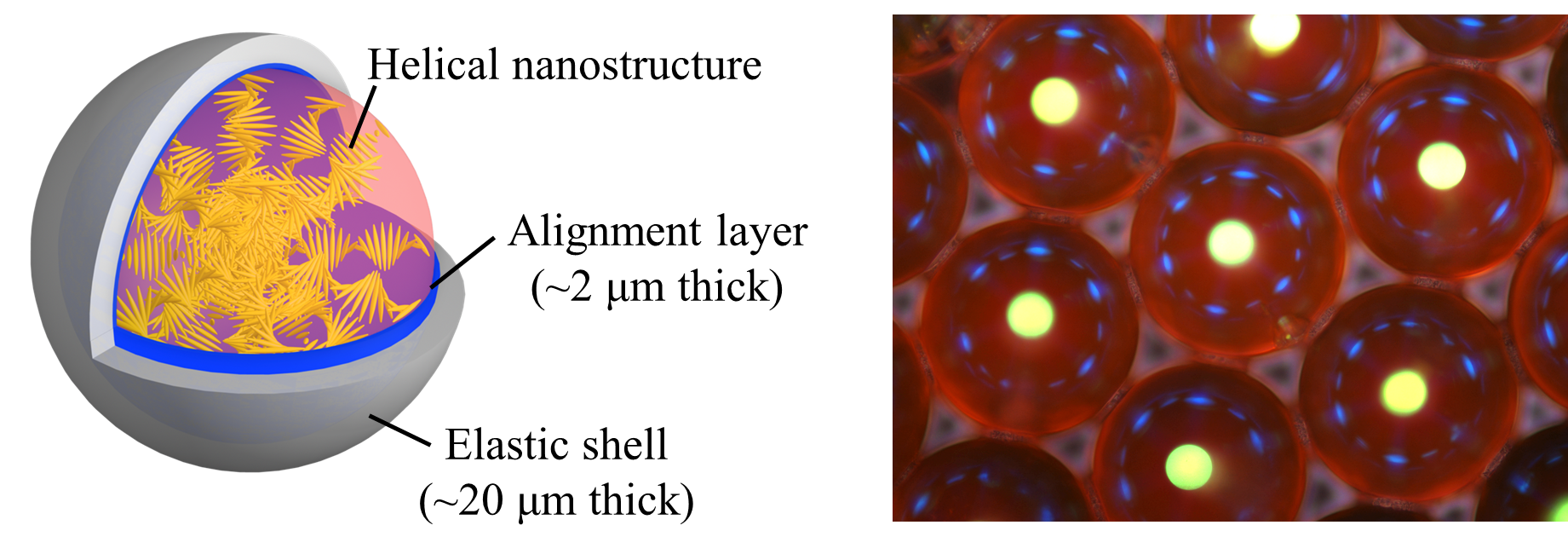
Figure 2. Composition (left panel) and optical microscopy image (right panel) of the capsule-type laser resonator
-
research A Novel Material for Transparent and Flexible Displays
(Research team led by Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry) The next generation of flexible and transparent displays will require a high-performing and flexible polymeric material that has the optical and thermal properties of glass. The material must be transparent to visible light and have a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). Unfortunately, such a polymeric material has not been available. A KAIST research team has succeeded in making a new polymeric mat
2019-01-24 -
research Successful Synthesis of Gamma-Lanctam Rings from Hydrocarbons
(The team of Professor Chang, far right, at the Department of Chemistry) KAIST chemists have designed a novel strategy to synthesize ring-shaped cyclic molecules, highly sought-after by pharmaceutical and chemical industries, and known as gamma-lactams. This study describes how these five-membered rings can be prepared from inexpensive and readily available feedstock hydrocarbons, as well as from complex organic molecules, such as amino acids and steroids. Gamma-lactams find several app
2018-03-02 -
research Structural Insight into the Molecular Mechanism of PET Degradation
A KAIST metabolic engineering research team has newly suggested a molecular mechanism showing superior degradability of poly ethylene terephthalate (PET). This is the first report to simultaneously determine the 3D crystal structure of Ideonella sakaiensis PETase and develop the new variant with enhanced PET degradation. Recently, diverse research projects are working to address the non-degradability of materials. A poly ethylene terephthalate (PET)-degrading bacterium called Ideonella sa
2018-01-31 -
research Study Identifies the Novel Molecular Signal for Triggering Septic Shock
Professor Seyun Kim’s team at the Department of Biological Sciences reported the mechanism by which cellular signaling transduction networks are precisely controlled in mediating innate immune responses, such as sepsis, by the enzyme IPMK (Inositol polyphosphate multikinase) which is essential for inositol biosynthesis metabolism. In collaboration with Professor Hyun Seong Roh at Seoul National University, the study’s first author, Eunha Kim, a Ph.D. candidate in Department of
2017-05-11 -
research Expanding the Genetic Code of Mus Musculus
Professor Hee-Sung Park of the Department of Chemistry, who garnered attention for his novel strategy of installing authentic post-translational modifications into recombinant proteins, expanded his research portfolio to another level. Professor Park’s team was the first to report the generation of a mouse strain with an expanded genetic code, allowing site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids. Professor Park published the research on the new chemical biology method for achiev
2017-03-27