Nature
-
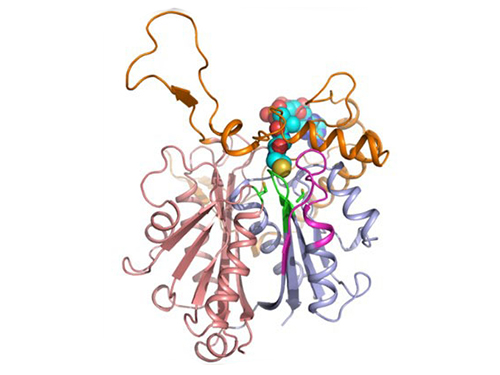 Discovery of Redox-Switch of KEenzyme Involved in N-Butanol Biosynthesis
Research teams at KAIST and Kyungpook National University (KNU) have succeeded in uncovering the redox-switch of thiolase, a key enzyme for n-butanol production in Clostridium acetobutylicum, one of the best known butanol-producing bacteria.
Biological n-butanol production was first reported by Louis Pasteur in 1861, and the bioprocess was industrialized usingClostridium acetobutylicum. The fermentation process by Clostridium strains has been known to be the most efficient one for n-butanol production. Due to growing world-wide issues such as energy security and climate change, the biological production of n-butanol has been receiving much renewed interest. This is because n-butanol possesses much better fuel characteristics compared to ethanol, such as higher energy content (29.2 MJ/L vs 19.6 MJ/L), less corrosiveness, less hygroscopy, and the ease with which it can be blended with gasoline and diesel.
In the paper published in Nature Communications, a broad-scope, online-only, and open access journal issued by the Nature Publishing Group (NPG), on September 22, 2015, Professor Kyung-Jin Kim at the School of Life Sciences, KNU, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, have proved that the redox-switch of thiolase plays a role in a regulation of metabolic flux in C. acetobutylicum by using in silico modeling and simulation tools.
The research team has redesigned thiolase with enhanced activity on the basis of the 3D structure of the wild-type enzyme. To reinforce a metabolic flux toward butanol production, the metabolic network of C. acetobutylicum strain was engineered with the redesigned enzyme. The combination of the discovery of 3D enzyme structure and systems metabolic engineering approaches resulted in increased n-butanol production in C. acetobutylicum, which allows the production of this important industrial chemical to be cost competitive.
Professors Kim and Lee said, "We have reported the 3D structure of C. acetobutylicum thiolase-a key enzyme involved in n-butanol biosynthesis, for the first time. Further study will be done to produce butanol more economically on the basis of the 3D structure of C. acetobutylicum thiolase."
This work was published online in Nature Communications on September 22, 2015.
Reference: Kim et al. "Redox-switch regulatory mechanism of thiolase from Clostridium acetobutylicum," Nature Communications
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Korea, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Advanced Biomass Center through the Global Frontier Research Program of the MEST, Korea.
For further information, contact Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, +82-42-350-3930); and Dr. Kyung-Jin Kim, Professor, KNU, Daegu, Korea (kkim@knu.ac.kr, +82-53-950-6088).
Figure 1: A redox-switch of thiolase involves in butanol biosynthesis in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Thiolase condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules for initiating four carbon flux towards butanol.
Figure 2: Thiolase catalyzes the condensation reaction of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA. Two catalytic cysteine residues at 88th and 378th are oxidized and formed an intermolecular disulfide bond in an oxidized status, which results in inactivation of the enzyme for n-butanol biosynthesis. The intermolecular disulfide bond is broken enabling the n-butanol biosynthesis, when the environment status is reduced.
2015.09.23 View 9722
Discovery of Redox-Switch of KEenzyme Involved in N-Butanol Biosynthesis
Research teams at KAIST and Kyungpook National University (KNU) have succeeded in uncovering the redox-switch of thiolase, a key enzyme for n-butanol production in Clostridium acetobutylicum, one of the best known butanol-producing bacteria.
Biological n-butanol production was first reported by Louis Pasteur in 1861, and the bioprocess was industrialized usingClostridium acetobutylicum. The fermentation process by Clostridium strains has been known to be the most efficient one for n-butanol production. Due to growing world-wide issues such as energy security and climate change, the biological production of n-butanol has been receiving much renewed interest. This is because n-butanol possesses much better fuel characteristics compared to ethanol, such as higher energy content (29.2 MJ/L vs 19.6 MJ/L), less corrosiveness, less hygroscopy, and the ease with which it can be blended with gasoline and diesel.
In the paper published in Nature Communications, a broad-scope, online-only, and open access journal issued by the Nature Publishing Group (NPG), on September 22, 2015, Professor Kyung-Jin Kim at the School of Life Sciences, KNU, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, have proved that the redox-switch of thiolase plays a role in a regulation of metabolic flux in C. acetobutylicum by using in silico modeling and simulation tools.
The research team has redesigned thiolase with enhanced activity on the basis of the 3D structure of the wild-type enzyme. To reinforce a metabolic flux toward butanol production, the metabolic network of C. acetobutylicum strain was engineered with the redesigned enzyme. The combination of the discovery of 3D enzyme structure and systems metabolic engineering approaches resulted in increased n-butanol production in C. acetobutylicum, which allows the production of this important industrial chemical to be cost competitive.
Professors Kim and Lee said, "We have reported the 3D structure of C. acetobutylicum thiolase-a key enzyme involved in n-butanol biosynthesis, for the first time. Further study will be done to produce butanol more economically on the basis of the 3D structure of C. acetobutylicum thiolase."
This work was published online in Nature Communications on September 22, 2015.
Reference: Kim et al. "Redox-switch regulatory mechanism of thiolase from Clostridium acetobutylicum," Nature Communications
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Korea, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Advanced Biomass Center through the Global Frontier Research Program of the MEST, Korea.
For further information, contact Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, +82-42-350-3930); and Dr. Kyung-Jin Kim, Professor, KNU, Daegu, Korea (kkim@knu.ac.kr, +82-53-950-6088).
Figure 1: A redox-switch of thiolase involves in butanol biosynthesis in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Thiolase condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules for initiating four carbon flux towards butanol.
Figure 2: Thiolase catalyzes the condensation reaction of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA. Two catalytic cysteine residues at 88th and 378th are oxidized and formed an intermolecular disulfide bond in an oxidized status, which results in inactivation of the enzyme for n-butanol biosynthesis. The intermolecular disulfide bond is broken enabling the n-butanol biosynthesis, when the environment status is reduced.
2015.09.23 View 9722 -
 Nature Biotechnology Nominates Sang Yup Lee of KAIST for Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014
Nature Biotechnology, recognized as the most prestigious journal in the field of biotechnology, has released today its list of the Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology) ranked seventh in the list. He is the only Asian researcher listed.
The journal, in partnership with IP Checkups, a patent analytics firm, presents an annual ranking of researchers based on their paper and patent output. The list includes, among others, each researcher’s most-cited patent in the past five years and their H index, a measurement to evaluate the impact of a researcher’s published work utilizing citation analysis. (More details can be found at http://www.nature.com/bioent/2015/150801/full/bioe.2015.9.html.)
American institutions made up the majority of the list, with 18 universities and research institutes, and the remainder was filled by KAIST in Korea and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) in Australia.
Globally known as a leading researcher in systems metabolic engineering, Professor Lee has published more than 500 journal papers and 580 patents. He has received many awards, including the Citation Classic Award, Elmer Gaden Award, Merck Metabolic Engineering Award, ACS Marvin Johnson Award, SIMB Charles Thom Award, POSCO TJ Park Prize, Amgen Biochemical Engineering Award, and the Ho Am Prize in Engineering.
2015.08.27 View 8688
Nature Biotechnology Nominates Sang Yup Lee of KAIST for Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014
Nature Biotechnology, recognized as the most prestigious journal in the field of biotechnology, has released today its list of the Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology) ranked seventh in the list. He is the only Asian researcher listed.
The journal, in partnership with IP Checkups, a patent analytics firm, presents an annual ranking of researchers based on their paper and patent output. The list includes, among others, each researcher’s most-cited patent in the past five years and their H index, a measurement to evaluate the impact of a researcher’s published work utilizing citation analysis. (More details can be found at http://www.nature.com/bioent/2015/150801/full/bioe.2015.9.html.)
American institutions made up the majority of the list, with 18 universities and research institutes, and the remainder was filled by KAIST in Korea and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) in Australia.
Globally known as a leading researcher in systems metabolic engineering, Professor Lee has published more than 500 journal papers and 580 patents. He has received many awards, including the Citation Classic Award, Elmer Gaden Award, Merck Metabolic Engineering Award, ACS Marvin Johnson Award, SIMB Charles Thom Award, POSCO TJ Park Prize, Amgen Biochemical Engineering Award, and the Ho Am Prize in Engineering.
2015.08.27 View 8688 -
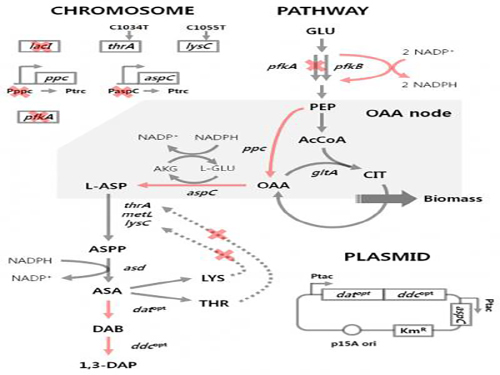 'Engineered Bacterium Produces 1,3-Diaminopropane'
A research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported, for the first time, the production of 1,3-diaminopropane via fermentation of an engineered bacterium.
1,3-Diaminopropane is a three carbon diamine, which has a wide range of industrial applications including epoxy resin and cross-linking agents, as well as precursors for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and organic chemicals. It can also be polymerized with dicarboxylic acids to make polyamides (nylons) for use as engineering plastics, medical materials, and adhesives.
Traditionally, 1,3-diaminopropane is derived from petroleum-based processes. In effort to address critical problems such as the depletion of petroleum and environmental issues inherent to the petroleum-based processes, the research team has developed an Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain capable of producing 1,3-diaminopropane. Using this technology, 1,3-diaminopropane can now be produced from renewable biomass instead of petroleum.
E. coli as found in nature is unable to produce 1,3-diaminopropane. Metabolic engineering, a technology to transform microorganisms into highly efficient microbial cell factories capable of producing chemical compounds of interest, was utilized to engineer the E. coli strain. First, naturally existing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of 1,3-diaminopropane were introduced into a virtual cell in silico to determine the most efficient metabolic pathway for the 1,3-diaminopropane production. The metabolic pathway selected was then introduced into an E. coli strain and successfully produced 1,3-diaminopropane for the first time in the world.
The research team applied metabolic engineering additionally, and the production titer of 1,3-diaminopropane increased about 21 fold. The Fed-batch fermentation of the engineered E. coli strain produced 13 grams per liter of 1,3-diaminoproapne. With this technology, 1,3-diaminopropane can be produced using renewable biomass, and it will be the starting point for replacing the current petroleum-based processes with bio-based processes.
Professor Lee said, “Our study suggested a possibility to produce 1,3-diaminopropane based on biorefinery. Further study will be done to increase the titer and productivity of 1,3-diaminopropane.”
This work was published online in Scientific Reports on August 11, 2015.
Reference: Chae, T.U. et al. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1,3-diaminopropane, a three carbon diamine," Scientific Reports:
http://www.nature.com/articles/srep13040
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Figure 1: Metabolic engineering strategies for 1,3-diaminopropane production using C4 pathway
Figure 2: Fed-batch fermentation profiles of two final engineered E. coli strains
2015.08.12 View 10008
'Engineered Bacterium Produces 1,3-Diaminopropane'
A research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported, for the first time, the production of 1,3-diaminopropane via fermentation of an engineered bacterium.
1,3-Diaminopropane is a three carbon diamine, which has a wide range of industrial applications including epoxy resin and cross-linking agents, as well as precursors for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and organic chemicals. It can also be polymerized with dicarboxylic acids to make polyamides (nylons) for use as engineering plastics, medical materials, and adhesives.
Traditionally, 1,3-diaminopropane is derived from petroleum-based processes. In effort to address critical problems such as the depletion of petroleum and environmental issues inherent to the petroleum-based processes, the research team has developed an Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain capable of producing 1,3-diaminopropane. Using this technology, 1,3-diaminopropane can now be produced from renewable biomass instead of petroleum.
E. coli as found in nature is unable to produce 1,3-diaminopropane. Metabolic engineering, a technology to transform microorganisms into highly efficient microbial cell factories capable of producing chemical compounds of interest, was utilized to engineer the E. coli strain. First, naturally existing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of 1,3-diaminopropane were introduced into a virtual cell in silico to determine the most efficient metabolic pathway for the 1,3-diaminopropane production. The metabolic pathway selected was then introduced into an E. coli strain and successfully produced 1,3-diaminopropane for the first time in the world.
The research team applied metabolic engineering additionally, and the production titer of 1,3-diaminopropane increased about 21 fold. The Fed-batch fermentation of the engineered E. coli strain produced 13 grams per liter of 1,3-diaminoproapne. With this technology, 1,3-diaminopropane can be produced using renewable biomass, and it will be the starting point for replacing the current petroleum-based processes with bio-based processes.
Professor Lee said, “Our study suggested a possibility to produce 1,3-diaminopropane based on biorefinery. Further study will be done to increase the titer and productivity of 1,3-diaminopropane.”
This work was published online in Scientific Reports on August 11, 2015.
Reference: Chae, T.U. et al. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1,3-diaminopropane, a three carbon diamine," Scientific Reports:
http://www.nature.com/articles/srep13040
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Figure 1: Metabolic engineering strategies for 1,3-diaminopropane production using C4 pathway
Figure 2: Fed-batch fermentation profiles of two final engineered E. coli strains
2015.08.12 View 10008 -
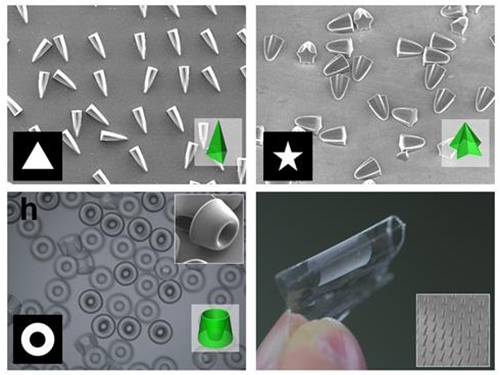 Novel Photolithographic Technology Enabling 3D Control over Functional Shapes of Microstructures
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim and his research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have developed a novel photolithographic technology enabling control over the functional shapes of micropatterns using oxygen diffusion.
The research was published online in the March 13th issue of Nature Communications and was selected as a featured image for the journal.
Photolithography is a standard optical process for transferring micropatterns on to a substrate by exposing specific regions of the photoresist layer to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used widely throughout industries that require micropatterns, especially in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Conventional photolithography relied on photomasks which protected certain regions of the substrate from the input UV light. Areas covered by the photomasks remain intact with the base layer while the areas exposed to the UV light are washed away, thus creating a micropattern. This technology was limited to a two-dimensional, disc-shaped design as the boundaries between the exposed and roofed regions are always in a parallel arrangement with the direction of the light.
Professor Kim’s research team discovered that: 1) the areas exposed to UV light lowered the concentration of oxygen and thus resulted in oxygen diffusion; and 2) manipulation of the diffusion speed and direction allowed control of the growth, shape and size of the polymers. Based on these findings, the team developed a new photolithographic technology that enabled the production of micropatterns with three-dimensional structures in various shapes and sizes.
Oxygen was considered an inhibitor during photopolymerization. Photoresist under UV light creates radicals which initialize a chemical reaction. These radicals are eliminated with the presence of oxygen and thus prevents the reaction. This suggests that the photoresist must be exposed to UV light for an extended time to completely remove oxygen for a chemical reaction to begin.
The research team, however, exploited the presence of oxygen. While the region affected by the UV light lowered oxygen concentration, the concentration in the untouched region remained unchanged. This difference in the concentrations caused a diffusion of oxygen to the region under UV light.
When the speed of the oxygen flow is slow, the diffusion occurs in parallel with the direction of the UV light. When fast, the diffusion process develops horizontally, outward from the area affected by the UV light. Professor Kim and his team proved this phenomenon both empirically and theoretically. Furthermore, by injecting an external oxygen source, the team was able to manipulate diffusion strength and direction, and thus control the shape and size of the polymer. The use of the polymerization inhibitors enabled and facilitated the fabrication of complex, three-dimensional micropatterns.
Professor Kim said, “While 3D printing is considered an innovative manufacturing technology, it cannot be used for mass-production of microscopic products. The new photolithographic technology will have a broad impact on both the academia and industry especially because existing, conventional photolithographic equipment can be used for the development of more complex micropatterns.” His newest technology will enhance the manufacturing process of three-dimensional polymers which were considered difficult to be commercialized.
The research was also dedicated to the late Professor Seung-Man Yang of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. He was considered one of the greatest scholars in Korea in the field of hydrodynamics and colloids.
Picture 1: Featured Image of Nature Communications, March 2015
Picture 2: Polymers with various shapes and sizes produced with the new photolithographic technology developed by Professor Kim
2015.04.06 View 9606
Novel Photolithographic Technology Enabling 3D Control over Functional Shapes of Microstructures
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim and his research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have developed a novel photolithographic technology enabling control over the functional shapes of micropatterns using oxygen diffusion.
The research was published online in the March 13th issue of Nature Communications and was selected as a featured image for the journal.
Photolithography is a standard optical process for transferring micropatterns on to a substrate by exposing specific regions of the photoresist layer to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used widely throughout industries that require micropatterns, especially in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Conventional photolithography relied on photomasks which protected certain regions of the substrate from the input UV light. Areas covered by the photomasks remain intact with the base layer while the areas exposed to the UV light are washed away, thus creating a micropattern. This technology was limited to a two-dimensional, disc-shaped design as the boundaries between the exposed and roofed regions are always in a parallel arrangement with the direction of the light.
Professor Kim’s research team discovered that: 1) the areas exposed to UV light lowered the concentration of oxygen and thus resulted in oxygen diffusion; and 2) manipulation of the diffusion speed and direction allowed control of the growth, shape and size of the polymers. Based on these findings, the team developed a new photolithographic technology that enabled the production of micropatterns with three-dimensional structures in various shapes and sizes.
Oxygen was considered an inhibitor during photopolymerization. Photoresist under UV light creates radicals which initialize a chemical reaction. These radicals are eliminated with the presence of oxygen and thus prevents the reaction. This suggests that the photoresist must be exposed to UV light for an extended time to completely remove oxygen for a chemical reaction to begin.
The research team, however, exploited the presence of oxygen. While the region affected by the UV light lowered oxygen concentration, the concentration in the untouched region remained unchanged. This difference in the concentrations caused a diffusion of oxygen to the region under UV light.
When the speed of the oxygen flow is slow, the diffusion occurs in parallel with the direction of the UV light. When fast, the diffusion process develops horizontally, outward from the area affected by the UV light. Professor Kim and his team proved this phenomenon both empirically and theoretically. Furthermore, by injecting an external oxygen source, the team was able to manipulate diffusion strength and direction, and thus control the shape and size of the polymer. The use of the polymerization inhibitors enabled and facilitated the fabrication of complex, three-dimensional micropatterns.
Professor Kim said, “While 3D printing is considered an innovative manufacturing technology, it cannot be used for mass-production of microscopic products. The new photolithographic technology will have a broad impact on both the academia and industry especially because existing, conventional photolithographic equipment can be used for the development of more complex micropatterns.” His newest technology will enhance the manufacturing process of three-dimensional polymers which were considered difficult to be commercialized.
The research was also dedicated to the late Professor Seung-Man Yang of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. He was considered one of the greatest scholars in Korea in the field of hydrodynamics and colloids.
Picture 1: Featured Image of Nature Communications, March 2015
Picture 2: Polymers with various shapes and sizes produced with the new photolithographic technology developed by Professor Kim
2015.04.06 View 9606 -
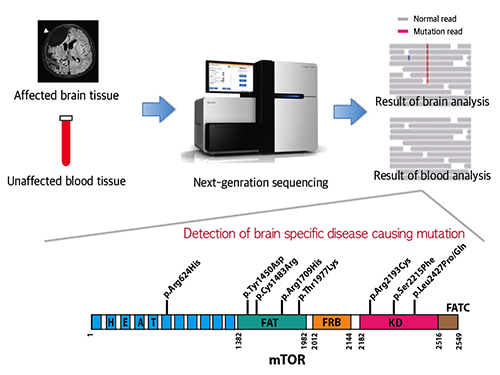 Mutations Occurring Only in Brain Responsible for Intractable Epilepsy Identified
KAIST researchers have discovered that brain somatic mutations in MTOR gene induce intractable epilepsy and suggest a precision medicine to treat epileptic seizures.
Epilepsy is a brain disorder which afflicts more than 50 million people worldwide. Many epilepsy patients can control their symptoms through medication, but about 30% suffer from intractable epilepsy and are unable to manage the disease with drugs. Intractable epilepsy causes multiple seizures, permanent mental, physical, and developmental disabilities, and even death. Therefore, surgical removal of the affected area from the brain has been practiced as a treatment for patients with medically refractory seizures, but this too fails to provide a complete solution because only 60% of the patients who undergo surgery are rendered free of seizures.
A Korean research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Professor Dong-Seok Kim of Epilepsy Research Center at Yonsei University College of Medicine has recently identified brain somatic mutations in the gene of mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) as the cause of focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCDII), one of the most important and common inducers to intractable epilepsy, particularly in children. They propose a targeted therapy to lessen epileptic seizures by suppressing the activation of mTOR kinase, a signaling protein in the brain. Their research results were published online in Nature Medicine on March 23, 2015.
FCDII contributes to the abnormal developments of the cerebral cortex, ranging from cortical disruption to severe forms of cortical dyslamination, balloon cells, and dysplastic neurons. The research team studied 77 FCDII patients with intractable epilepsy who had received a surgery to remove the affected regions from the brain. The researchers used various deep sequencing technologies to conduct comparative DNA analysis of the samples obtained from the patients’ brain and blood, or saliva. They reported that about 16% of the studied patients had somatic mutations in their brain. Such mutations, however, did not take place in their blood or saliva DNA.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee of KAIST said, “This is an important finding. Unlike our previous belief that genetic mutations causing intractable epilepsy exist anywhere in the human body including blood, specific gene mutations incurred only in the brain can lead to intractable epilepsy. From our animal models, we could see how a small fraction of mutations carrying neurons in the brain could affect its entire function.”
The research team recapitulated the pathogenesis of intractable epilepsy by inducing the focal cortical expression of mutated mTOR in the mouse brain via electroporation method and observed as the mouse develop epileptic symptoms. They then treated these mice with the drug called “rapamycin” to inhibit the activity of mTOR protein and observed that it suppressed the development of epileptic seizures with cytomegalic neurons.
“Our study offers the first evidence that brain-somatic activating mutations in MTOR cause FCDII and identifies mTOR as a treatment target for intractable epilepsy,” said co-author Dr. Dong-Seok Kim, a neurosurgeon at Yonsei Medical Center with the country’s largest surgical experiences in treating patients with this condition.
The research paper is titled “Brain somatic mutations in MTOR cause focal cortical dysplasia type II leading to intractable epilepsy.” (Digital Object Identifier #: 10.1038/nm.3824)
Picture 1: A schematic image to show how to detect brain specific mutation using next-generation sequencing technology with blood-brain paired sample. Simple comparison of non-overlapping mutations between affected and unaffected tissues is able to detect brain specific mutations.
Picture 2: A schematic image to show how to generate focal cortical dysplasia mouse model. This mouse model open the new window of drug screening for seizure patients.
Picture 3: Targeted medicine can rescue the focal cortical dysplasia symptoms including cytomegalic neuron & intractable epilepsy.
2015.03.25 View 13168
Mutations Occurring Only in Brain Responsible for Intractable Epilepsy Identified
KAIST researchers have discovered that brain somatic mutations in MTOR gene induce intractable epilepsy and suggest a precision medicine to treat epileptic seizures.
Epilepsy is a brain disorder which afflicts more than 50 million people worldwide. Many epilepsy patients can control their symptoms through medication, but about 30% suffer from intractable epilepsy and are unable to manage the disease with drugs. Intractable epilepsy causes multiple seizures, permanent mental, physical, and developmental disabilities, and even death. Therefore, surgical removal of the affected area from the brain has been practiced as a treatment for patients with medically refractory seizures, but this too fails to provide a complete solution because only 60% of the patients who undergo surgery are rendered free of seizures.
A Korean research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Professor Dong-Seok Kim of Epilepsy Research Center at Yonsei University College of Medicine has recently identified brain somatic mutations in the gene of mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) as the cause of focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCDII), one of the most important and common inducers to intractable epilepsy, particularly in children. They propose a targeted therapy to lessen epileptic seizures by suppressing the activation of mTOR kinase, a signaling protein in the brain. Their research results were published online in Nature Medicine on March 23, 2015.
FCDII contributes to the abnormal developments of the cerebral cortex, ranging from cortical disruption to severe forms of cortical dyslamination, balloon cells, and dysplastic neurons. The research team studied 77 FCDII patients with intractable epilepsy who had received a surgery to remove the affected regions from the brain. The researchers used various deep sequencing technologies to conduct comparative DNA analysis of the samples obtained from the patients’ brain and blood, or saliva. They reported that about 16% of the studied patients had somatic mutations in their brain. Such mutations, however, did not take place in their blood or saliva DNA.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee of KAIST said, “This is an important finding. Unlike our previous belief that genetic mutations causing intractable epilepsy exist anywhere in the human body including blood, specific gene mutations incurred only in the brain can lead to intractable epilepsy. From our animal models, we could see how a small fraction of mutations carrying neurons in the brain could affect its entire function.”
The research team recapitulated the pathogenesis of intractable epilepsy by inducing the focal cortical expression of mutated mTOR in the mouse brain via electroporation method and observed as the mouse develop epileptic symptoms. They then treated these mice with the drug called “rapamycin” to inhibit the activity of mTOR protein and observed that it suppressed the development of epileptic seizures with cytomegalic neurons.
“Our study offers the first evidence that brain-somatic activating mutations in MTOR cause FCDII and identifies mTOR as a treatment target for intractable epilepsy,” said co-author Dr. Dong-Seok Kim, a neurosurgeon at Yonsei Medical Center with the country’s largest surgical experiences in treating patients with this condition.
The research paper is titled “Brain somatic mutations in MTOR cause focal cortical dysplasia type II leading to intractable epilepsy.” (Digital Object Identifier #: 10.1038/nm.3824)
Picture 1: A schematic image to show how to detect brain specific mutation using next-generation sequencing technology with blood-brain paired sample. Simple comparison of non-overlapping mutations between affected and unaffected tissues is able to detect brain specific mutations.
Picture 2: A schematic image to show how to generate focal cortical dysplasia mouse model. This mouse model open the new window of drug screening for seizure patients.
Picture 3: Targeted medicine can rescue the focal cortical dysplasia symptoms including cytomegalic neuron & intractable epilepsy.
2015.03.25 View 13168 -
 KAIST Develops Ultrathin Polymer Insulators Key to Low-Power Soft Electronics
Using an initiated chemical vapor deposition technique, the research team created an ultrathin polymeric insulating layer essential in realizing transistors with flexibility and low power consumption. This advance is expected to accelerate the commercialization of wearable and soft electronics.
A group of researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a high-performance ultrathin polymeric insulator for field-effect transistors (FETs). The researchers used vaporized monomers to form polymeric films grown conformally on various surfaces including plastics to produce a versatile insulator that meets a wide range of requirements for next-generation electronic devices. Their research results were published online in Nature Materials on March 9th, 2015.
FETs are an essential component for any modern electronic device used in our daily life from cell phones and computers, to flat-panel displays. Along with three electrodes (gate, source, and drain), FETs consist of an insulating layer and a semiconductor channel layer. The insulator in FETs plays an important role in controlling the conductance of the semiconductor channel and thus current flow within the translators. For reliable and low-power operation of FETs, electrically robust, ultrathin insulators are essential. Conventionally, such insulators are made of inorganic materials (e.g., oxides and nitrides) built on a hard surface such as silicon or glass due to their excellent insulating performance and reliability.
However, these insulators were difficult to implement into soft electronics due to their rigidity and high process temperature. In recent years, many researchers have studied polymers as promising insulating materials that are compatible with soft unconventional substrates and emerging semiconductor materials. The traditional technique employed in developing a polymer insulator, however, had the limitations of low surface coverage at ultra-low thickness, hindering FETs adopting polymeric insulators from operating at low voltage.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Sung Gap Im of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department and Professor Seunghyup Yoo and Professor Byung Jin Cho of the Electrical Engineering Department developed an insulating layer of organic polymers, “pV3D3,” that can be greatly scaled down, without losing its ideal insulating properties, to a thickness of less than 10 nanometers (nm) using the all-dry vapor-phase technique called the “initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD).”
The iCVD process allows gaseous monomers and initiators to react with each other in a low vacuum condition, and as a result, conformal polymeric films with excellent insulating properties are deposited on a substrate. Unlike the traditional technique, the surface-growing character of iCVD can overcome the problems associated with surface tension and produce highly uniform and pure ultrathin polymeric films over a large area with virtually no surface or substrate limitations. Furthermore, most iCVD polymers are created at room temperature, which lessens the strain exerted upon and damage done to the substrates.
With the pV3D3 insulator, the research team built low-power, high-performance FETs based on various semiconductor materials such as organics, graphene, and oxides, demonstrating the pV3D3 insulator’s wide range of material compatibility. They also manufactured a stick-on, removable electronic component using conventional packaging tape as a substrate. In collaboration with Professor Yong-Young Noh from Dongguk University in Korea, the team successfully developed a transistor array on a large-scale flexible substrate with the pV3D3 insulator.
Professor Im said, “The down-scalability and wide range of compatibility observed with iCVD-grown pV3D3 are unprecedented for polymeric insulators. Our iCVD pV3D3 polymeric films showed an insulating performance comparable to that of inorganic insulating layers, even when their thickness were scaled down to sub-10 nm. We expect our development will greatly benefit flexible or soft electronics, which will play a key role in the success of emerging electronic devices such as wearable computers.”
The title of the research paper is “Synthesis of ultrathin polymer insulating layers by initiated chemical vapor deposition for low-power soft electronics” (Digital Object Identifier (DOI) number is 10.1038/nmat4237).
Picture 1: A schematic image to show how the initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) technique produces pV3D3 polymeric films: (i) introduction of vaporized monomers and initiators, (ii) activation of initiators to thermally dissociate into radicals, (iii) adsorption of monomers and initiator radicals onto a substrate, and (iv) transformation of free-radical polymerization into pV3D3 thin films.
Picture 2: This is a transistor array fabricated on a large scale, highly flexible substrate with pV3D3 polymeric films.
Picture 3: This photograph shows an electronic component fabricated on a conventional packaging tape, which is attachable or detachable, with pV3D3 polymeric films embedded.
2015.03.10 View 12316
KAIST Develops Ultrathin Polymer Insulators Key to Low-Power Soft Electronics
Using an initiated chemical vapor deposition technique, the research team created an ultrathin polymeric insulating layer essential in realizing transistors with flexibility and low power consumption. This advance is expected to accelerate the commercialization of wearable and soft electronics.
A group of researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a high-performance ultrathin polymeric insulator for field-effect transistors (FETs). The researchers used vaporized monomers to form polymeric films grown conformally on various surfaces including plastics to produce a versatile insulator that meets a wide range of requirements for next-generation electronic devices. Their research results were published online in Nature Materials on March 9th, 2015.
FETs are an essential component for any modern electronic device used in our daily life from cell phones and computers, to flat-panel displays. Along with three electrodes (gate, source, and drain), FETs consist of an insulating layer and a semiconductor channel layer. The insulator in FETs plays an important role in controlling the conductance of the semiconductor channel and thus current flow within the translators. For reliable and low-power operation of FETs, electrically robust, ultrathin insulators are essential. Conventionally, such insulators are made of inorganic materials (e.g., oxides and nitrides) built on a hard surface such as silicon or glass due to their excellent insulating performance and reliability.
However, these insulators were difficult to implement into soft electronics due to their rigidity and high process temperature. In recent years, many researchers have studied polymers as promising insulating materials that are compatible with soft unconventional substrates and emerging semiconductor materials. The traditional technique employed in developing a polymer insulator, however, had the limitations of low surface coverage at ultra-low thickness, hindering FETs adopting polymeric insulators from operating at low voltage.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Sung Gap Im of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department and Professor Seunghyup Yoo and Professor Byung Jin Cho of the Electrical Engineering Department developed an insulating layer of organic polymers, “pV3D3,” that can be greatly scaled down, without losing its ideal insulating properties, to a thickness of less than 10 nanometers (nm) using the all-dry vapor-phase technique called the “initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD).”
The iCVD process allows gaseous monomers and initiators to react with each other in a low vacuum condition, and as a result, conformal polymeric films with excellent insulating properties are deposited on a substrate. Unlike the traditional technique, the surface-growing character of iCVD can overcome the problems associated with surface tension and produce highly uniform and pure ultrathin polymeric films over a large area with virtually no surface or substrate limitations. Furthermore, most iCVD polymers are created at room temperature, which lessens the strain exerted upon and damage done to the substrates.
With the pV3D3 insulator, the research team built low-power, high-performance FETs based on various semiconductor materials such as organics, graphene, and oxides, demonstrating the pV3D3 insulator’s wide range of material compatibility. They also manufactured a stick-on, removable electronic component using conventional packaging tape as a substrate. In collaboration with Professor Yong-Young Noh from Dongguk University in Korea, the team successfully developed a transistor array on a large-scale flexible substrate with the pV3D3 insulator.
Professor Im said, “The down-scalability and wide range of compatibility observed with iCVD-grown pV3D3 are unprecedented for polymeric insulators. Our iCVD pV3D3 polymeric films showed an insulating performance comparable to that of inorganic insulating layers, even when their thickness were scaled down to sub-10 nm. We expect our development will greatly benefit flexible or soft electronics, which will play a key role in the success of emerging electronic devices such as wearable computers.”
The title of the research paper is “Synthesis of ultrathin polymer insulating layers by initiated chemical vapor deposition for low-power soft electronics” (Digital Object Identifier (DOI) number is 10.1038/nmat4237).
Picture 1: A schematic image to show how the initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) technique produces pV3D3 polymeric films: (i) introduction of vaporized monomers and initiators, (ii) activation of initiators to thermally dissociate into radicals, (iii) adsorption of monomers and initiator radicals onto a substrate, and (iv) transformation of free-radical polymerization into pV3D3 thin films.
Picture 2: This is a transistor array fabricated on a large scale, highly flexible substrate with pV3D3 polymeric films.
Picture 3: This photograph shows an electronic component fabricated on a conventional packaging tape, which is attachable or detachable, with pV3D3 polymeric films embedded.
2015.03.10 View 12316 -
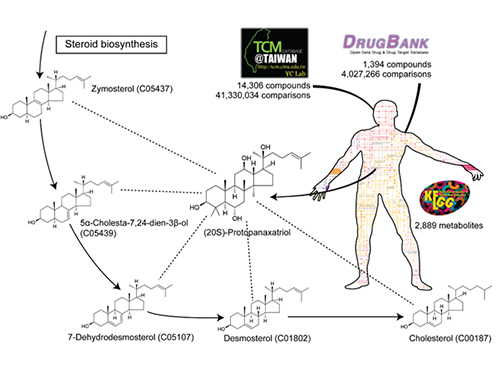 System Approach Using Metabolite Structural Similarity Toward TOM Suggested
A Korean research team at KAIST suggests that a system approach using metabolite structural similarity helps to elucidate the mechanisms of action of traditional oriental medicine.
Traditional oriental medicine (TOM) has been practiced in Asian countries for centuries, and is gaining increasing popularity around the world. Despite its efficacy in various symptoms, TOM has been practiced without precise knowledge of its mechanisms of action. Use of TOM largely comes from empirical knowledge practiced over a long period of time. The fact that some of the compounds found in TOM have led to successful modern drugs such as artemisinin for malaria and taxol (Paclitaxel) for cancer has spurred modernization of TOM.
A research team led by Sang-Yup Lee at KAIST has focused on structural similarities between compounds in TOM and human metabolites to help explain TOM’s mechanisms of action. This systems approach using structural similarities assumes that compounds which are structurally similar to metabolites could affect relevant metabolic pathways and reactions by biosynthesizing structurally similar metabolites.
Structural similarity analysis has helped to identify mechanisms of action of TOM. This is described in a recent study entitled “A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine,” published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 6, 2015. In this study, the research team conducted structural comparisons of all the structurally known compounds in TOM and human metabolites on a large-scale. As a control, structures of all available approved drugs were also compared against human metabolites. This structural analysis provides two important results. First, the identification of metabolites structurally similar to TOM compounds helped to narrow down the candidate target pathways and reactions for the effects from TOM compounds. Second, it suggested that a greater fraction of all the structurally known TOM compounds appeared to be more similar to human metabolites than the approved drugs. This second finding indicates that TOM has a great potential to interact with diverse metabolic pathways with strong efficacy. This finding, in fact, shows that TOM compounds might be advantageous for the multitargeting required to cure complex diseases. “Once we have narrowed down candidate target pathways and reactions using this structural similarity approach, additional in silico tools will be necessary to characterize the mechanisms of action of many TOM compounds at a molecular level,” said Hyun Uk Kim, a research professor at KAIST.
TOM’s multicomponent, multitarget approach wherein multiple components show synergistic effects to treat symptoms is highly distinctive. The researchers investigated previously observed effects recorded since 2000 of a set of TOM compounds with known mechanisms of action. TOM compounds’ synergistic combinations largely consist of a major compound providing the intended efficacy to the target site and supporting compounds which maximize the efficacy of the major compound. In fact, such combination designs appear to mirror the Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa design principle of TOM.
That principle, Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa (君臣佐使 or Jun-Chen-Zuo-Shi in Chinese) literally means “king-minister-assistant-ambassador.” In ancient East Asian medicine, treating human diseases and taking good care of the human body are analogous to the politics of governing a nation. Just as good governance requires that a king be supported by ministers, assistants and/or ambassadors, treating diseases or good care of the body required the combined use of herbal medicines designed based on the concept of Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa. Here, the Kun (king or the major component) indicates the major medicine (or herb) conveying the major drug efficacy, and is supported by three different types of medicines: the Shin (minister or the complementary component) for enhancing and/or complementing the efficacy of the Kun, Choa (assistant or the neutralizing component) for reducing any side effects caused by the Kun and reducing the minor symptoms accompanying major symptom, and Sa (ambassador or the delivery/retaining component) which facilitated the delivery of the Kun to the target site, and retaining the Kun for prolonged availability in the cells.
The synergistic combinations of TOM compounds reported in the literature showed four different types of synergisms: complementary action (similar to Kun-Shin), neutralizing action (similar to Kun-Choa), facilitating action or pharmacokinetic potentiation (both similar to Kun-Choa or Kun-Sa). Additional structural analyses for these compounds with synergism show that they appeared to affect metabolism of amino acids, co-factors and vitamins as major targets.
Professor Sang Yup Lee remarks, “This study lays a foundation for the integration of traditional oriental medicine with modern drug discovery and development. The systems approach taken in this analysis will be used to elucidate mechanisms of action of unknown TOM compounds which will then be subjected to rigorous validation through clinical and in silico experiments.”
Sources: Kim, H.U. et al. “A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine.” Nature Biotechnology. 33: 264-268 (2015).
This work was supported by the Bio-Synergy Research Project (2012M3A9C4048759) of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation. This work was also supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
The picture below presents the structural similarity analysis of comparing compounds in traditional oriental medicine and those in all available approved drugs against the structures of human metabolites.
2015.03.09 View 9346
System Approach Using Metabolite Structural Similarity Toward TOM Suggested
A Korean research team at KAIST suggests that a system approach using metabolite structural similarity helps to elucidate the mechanisms of action of traditional oriental medicine.
Traditional oriental medicine (TOM) has been practiced in Asian countries for centuries, and is gaining increasing popularity around the world. Despite its efficacy in various symptoms, TOM has been practiced without precise knowledge of its mechanisms of action. Use of TOM largely comes from empirical knowledge practiced over a long period of time. The fact that some of the compounds found in TOM have led to successful modern drugs such as artemisinin for malaria and taxol (Paclitaxel) for cancer has spurred modernization of TOM.
A research team led by Sang-Yup Lee at KAIST has focused on structural similarities between compounds in TOM and human metabolites to help explain TOM’s mechanisms of action. This systems approach using structural similarities assumes that compounds which are structurally similar to metabolites could affect relevant metabolic pathways and reactions by biosynthesizing structurally similar metabolites.
Structural similarity analysis has helped to identify mechanisms of action of TOM. This is described in a recent study entitled “A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine,” published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 6, 2015. In this study, the research team conducted structural comparisons of all the structurally known compounds in TOM and human metabolites on a large-scale. As a control, structures of all available approved drugs were also compared against human metabolites. This structural analysis provides two important results. First, the identification of metabolites structurally similar to TOM compounds helped to narrow down the candidate target pathways and reactions for the effects from TOM compounds. Second, it suggested that a greater fraction of all the structurally known TOM compounds appeared to be more similar to human metabolites than the approved drugs. This second finding indicates that TOM has a great potential to interact with diverse metabolic pathways with strong efficacy. This finding, in fact, shows that TOM compounds might be advantageous for the multitargeting required to cure complex diseases. “Once we have narrowed down candidate target pathways and reactions using this structural similarity approach, additional in silico tools will be necessary to characterize the mechanisms of action of many TOM compounds at a molecular level,” said Hyun Uk Kim, a research professor at KAIST.
TOM’s multicomponent, multitarget approach wherein multiple components show synergistic effects to treat symptoms is highly distinctive. The researchers investigated previously observed effects recorded since 2000 of a set of TOM compounds with known mechanisms of action. TOM compounds’ synergistic combinations largely consist of a major compound providing the intended efficacy to the target site and supporting compounds which maximize the efficacy of the major compound. In fact, such combination designs appear to mirror the Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa design principle of TOM.
That principle, Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa (君臣佐使 or Jun-Chen-Zuo-Shi in Chinese) literally means “king-minister-assistant-ambassador.” In ancient East Asian medicine, treating human diseases and taking good care of the human body are analogous to the politics of governing a nation. Just as good governance requires that a king be supported by ministers, assistants and/or ambassadors, treating diseases or good care of the body required the combined use of herbal medicines designed based on the concept of Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa. Here, the Kun (king or the major component) indicates the major medicine (or herb) conveying the major drug efficacy, and is supported by three different types of medicines: the Shin (minister or the complementary component) for enhancing and/or complementing the efficacy of the Kun, Choa (assistant or the neutralizing component) for reducing any side effects caused by the Kun and reducing the minor symptoms accompanying major symptom, and Sa (ambassador or the delivery/retaining component) which facilitated the delivery of the Kun to the target site, and retaining the Kun for prolonged availability in the cells.
The synergistic combinations of TOM compounds reported in the literature showed four different types of synergisms: complementary action (similar to Kun-Shin), neutralizing action (similar to Kun-Choa), facilitating action or pharmacokinetic potentiation (both similar to Kun-Choa or Kun-Sa). Additional structural analyses for these compounds with synergism show that they appeared to affect metabolism of amino acids, co-factors and vitamins as major targets.
Professor Sang Yup Lee remarks, “This study lays a foundation for the integration of traditional oriental medicine with modern drug discovery and development. The systems approach taken in this analysis will be used to elucidate mechanisms of action of unknown TOM compounds which will then be subjected to rigorous validation through clinical and in silico experiments.”
Sources: Kim, H.U. et al. “A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine.” Nature Biotechnology. 33: 264-268 (2015).
This work was supported by the Bio-Synergy Research Project (2012M3A9C4048759) of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation. This work was also supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
The picture below presents the structural similarity analysis of comparing compounds in traditional oriental medicine and those in all available approved drugs against the structures of human metabolites.
2015.03.09 View 9346 -
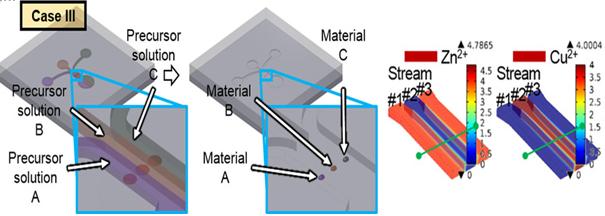 KAIST Develops Subminiature, Power-Efficient Air Pollution Sensing Probe
Professor Inkyu Park and his research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have developed a subminiature, power-efficient air-pollution sensing probe that can be applied to mobile devices. Their research findings were published online in the January 30th issue of Scientific Reports.
As air pollution has increased, people have taken greater interest in health care. The developed technology could allow people to measure independently the air pollution level of their surrounding environments.
Previous instruments used to measure air pollution levels were bulky and consumed a lot of power. They also often produced inaccurate results when measuring air pollution in which different toxic gases were mixed. These problems could not be resolved with existing semiconductor manufacturing process.
Using local temperature field control technology, Professor Park’s team succeeded in integrating multiple heterogeneous nanomaterials and fitting them onto a small, low-power electronic chip. This microheating sensor can heat microscale regions through local hydrothermal synthesis. Because it requires a miniscale amount of nanomaterials to manufacture, the sensor is most suitable for mobile devices.
Professor Park said, “Our research will contribute to the development of convergence technology in such field as air pollution sensing probes, biosensors, electronic devices, and displays.”
The team's research was supported by the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea.
Figure 1 – The Concept of Multiple Nanomaterial Device and Numerical Simulation Results of Precursor Solutions
Figure 2 - Multiple Nanomaterial Manufactured in a Microscale Region
2015.02.27 View 9440
KAIST Develops Subminiature, Power-Efficient Air Pollution Sensing Probe
Professor Inkyu Park and his research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have developed a subminiature, power-efficient air-pollution sensing probe that can be applied to mobile devices. Their research findings were published online in the January 30th issue of Scientific Reports.
As air pollution has increased, people have taken greater interest in health care. The developed technology could allow people to measure independently the air pollution level of their surrounding environments.
Previous instruments used to measure air pollution levels were bulky and consumed a lot of power. They also often produced inaccurate results when measuring air pollution in which different toxic gases were mixed. These problems could not be resolved with existing semiconductor manufacturing process.
Using local temperature field control technology, Professor Park’s team succeeded in integrating multiple heterogeneous nanomaterials and fitting them onto a small, low-power electronic chip. This microheating sensor can heat microscale regions through local hydrothermal synthesis. Because it requires a miniscale amount of nanomaterials to manufacture, the sensor is most suitable for mobile devices.
Professor Park said, “Our research will contribute to the development of convergence technology in such field as air pollution sensing probes, biosensors, electronic devices, and displays.”
The team's research was supported by the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea.
Figure 1 – The Concept of Multiple Nanomaterial Device and Numerical Simulation Results of Precursor Solutions
Figure 2 - Multiple Nanomaterial Manufactured in a Microscale Region
2015.02.27 View 9440 -
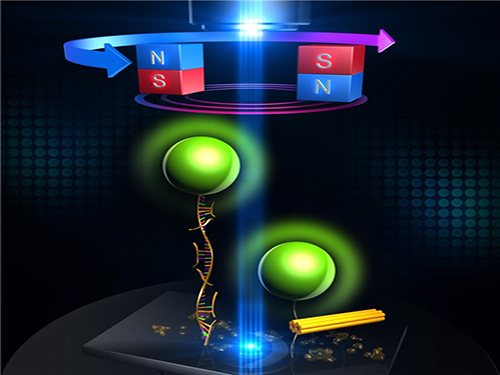 An Advanced Method of DNA Nanostructure Formation Developed
Professor Tae-Young Yoon’s research team from the Department of Physics at KAIST has developed a new method to form DNA nanostructures by using magnetic tweezers to observe and to induce the formation of the structure in real time.
Unlike traditional designs of "DNA origami" which relies on thermal or chemical annealing methods, the new technology utilizes a completely different dynamic in DNA folding. This allows the folding to be done within only ten minutes.
Developed in 2006, the "DNA origami" allows a long skeleton of DNA to be folded into an arbitrary structure by using small stapler DNA pieces. This has been a prominent method in DNA nanotechnology.
However, the traditional technology which adopts thermal processes could not control the DNA formation during the folding because every interaction among DNAs occurs simultaneously. Thus, the thermal processes, which take dozens of hours to complete, had to be repeated multiple times in order to find the optimal condition.
The research team designed a DNA folding using uni-molecular magnetic tweezers that applied force to a single DNA molecule while measuring the state of the DNA. Through this technology, they were able to induce the formation of DNA nanostructure and observe it at the same time.
During high temperature heat treatment, the first stage of conventional thermal processes, the internal structure of the long skeleton DNA untangles. To induce such state, after attaching one side of the skeleton DNA to the surface of glass and the other side to a magnetic material, the team unfolded the internal structure of the DNA by pulling the two sides apart with magnetic force.
Unlike the conventional thermal processes, this method lets the stapler DNA swiftly adhere to the skeleton DNA within a minute because the sites are revealed at room temperature.
After the stapler pieces connected to the skeleton, the team removed the magnetic force. Next, the structure folded through self-assembly as the stapler DNAs stuck to different sites on the skeleton DNA.
Professor Yoon said, “With the existing thermal methods, we could not differentiate the reactions of the DNA because the response of each DNA pieces mutually interacted with each other.” He added that “Using the magnetic tweezers, we were able to sort the process of DNA nanostructure formation into a series of reactions of DNA molecules that are well known, and shorten the time taken for formation in only ten minutes.”
He commented, “This nanostructure formation method will enable us to create more intricate and desirable DNA nanostructures by programming the folding of DNA origami structures.”
Conducted by Dr. Woori Bae under the guidance of Professor Yoon, the research findings were published online in the December 4th issue of Nature Communications.
Figure 1: Uni-molecular magnetic tweezers orchestrating the DNA nanostructure formation
Figure 2: The evolution of DNA nanostructure formation using magnetic tweezers. The DNA nanostructure with a 21-nanometer size was formed in about eight minutes.
2015.01.06 View 6899
An Advanced Method of DNA Nanostructure Formation Developed
Professor Tae-Young Yoon’s research team from the Department of Physics at KAIST has developed a new method to form DNA nanostructures by using magnetic tweezers to observe and to induce the formation of the structure in real time.
Unlike traditional designs of "DNA origami" which relies on thermal or chemical annealing methods, the new technology utilizes a completely different dynamic in DNA folding. This allows the folding to be done within only ten minutes.
Developed in 2006, the "DNA origami" allows a long skeleton of DNA to be folded into an arbitrary structure by using small stapler DNA pieces. This has been a prominent method in DNA nanotechnology.
However, the traditional technology which adopts thermal processes could not control the DNA formation during the folding because every interaction among DNAs occurs simultaneously. Thus, the thermal processes, which take dozens of hours to complete, had to be repeated multiple times in order to find the optimal condition.
The research team designed a DNA folding using uni-molecular magnetic tweezers that applied force to a single DNA molecule while measuring the state of the DNA. Through this technology, they were able to induce the formation of DNA nanostructure and observe it at the same time.
During high temperature heat treatment, the first stage of conventional thermal processes, the internal structure of the long skeleton DNA untangles. To induce such state, after attaching one side of the skeleton DNA to the surface of glass and the other side to a magnetic material, the team unfolded the internal structure of the DNA by pulling the two sides apart with magnetic force.
Unlike the conventional thermal processes, this method lets the stapler DNA swiftly adhere to the skeleton DNA within a minute because the sites are revealed at room temperature.
After the stapler pieces connected to the skeleton, the team removed the magnetic force. Next, the structure folded through self-assembly as the stapler DNAs stuck to different sites on the skeleton DNA.
Professor Yoon said, “With the existing thermal methods, we could not differentiate the reactions of the DNA because the response of each DNA pieces mutually interacted with each other.” He added that “Using the magnetic tweezers, we were able to sort the process of DNA nanostructure formation into a series of reactions of DNA molecules that are well known, and shorten the time taken for formation in only ten minutes.”
He commented, “This nanostructure formation method will enable us to create more intricate and desirable DNA nanostructures by programming the folding of DNA origami structures.”
Conducted by Dr. Woori Bae under the guidance of Professor Yoon, the research findings were published online in the December 4th issue of Nature Communications.
Figure 1: Uni-molecular magnetic tweezers orchestrating the DNA nanostructure formation
Figure 2: The evolution of DNA nanostructure formation using magnetic tweezers. The DNA nanostructure with a 21-nanometer size was formed in about eight minutes.
2015.01.06 View 6899 -
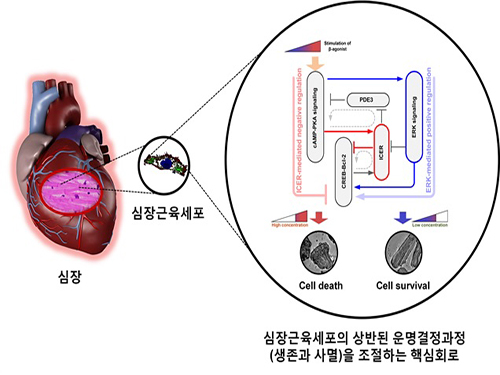 A Key Signal Transduction Pathway Switch in Cardiomyocyte Identified
A KAIST research team has identified the fundamental principle in deciding the fate of cardiomyocyte or heart muscle cells. They have determined that it depends on the degree of stimulus in β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway in the cardiomyocyte to control cells' survival or death. The findings, the team hopes, can be used to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.
The research was led by KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Chair Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and conducted by Dr. Sung-Young Shin (lead author) and Ph.D. candidates Ho-Sung Lee and Joon-Hyuk Kang. The research was conducted jointly with GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology) Department of Biological Sciences Professor Do-Han Kim’s team. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The paper was published in Nature Communications on December 17, 2014 with the title, “The switching role of β-adrenergic receptor signalling in cell survival or death decision of cardiomyocytes.”
The β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway can promote cell survival (mediated by β2 receptors), but also can result in cell death by inducing toxin (mediated by β1 receptors) that leads to various heart diseases including heart failure. Past attempts to identify the fundamental principle in the fate determining process of cardiomyocyte based on β-adrenergic receptor signalling concluded without much success.
The β-adrenergic receptor is a type of protein on the cell membrane of cardiomyocyte (heart muscle cell) that when stimulated by neurohormones such as epinephrine or norepinephrine would transduce signals making the cardiomyocyte contract faster and stronger.
The research team used large-scale computer simulation analysis and systems biology to identify ERK* and ICER** signal transduction pathways mediated by a feed-forward circuit as a key molecular switch that decides between cell survival and death.
Weak β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ERK signal transduction pathway, increasing Bcl-2*** protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte survival. On the other hand, strong β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ICER signal transduction pathway, reducing Bcl-2 protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte death.
Researchers used a systems biology approach to identify the mechanism of B-blocker****, a common drug prescribed for heart failure. When cardiomyocyte is treated with β1 inhibitor, strong stimulation on β-adrenergic receptor increases Bcl-2 expression, improving the chance of cardiomyocyte survival, a cell protection effect.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, “This research used systems biology, an integrated, convergence research of IT (information technology) and BT (biotechnology), to successfully identify the mechanism in deciding the fate of cardiomyocytes based on the β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway for the first time. I am hopeful that this research will enable the control of cardiomyocyte survival and death to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.”
Professor Cho’s team was the first to pioneer a new field of systems biology, especially concerning the complex signal transduction network involved in diseases. Their research is focused on modelling, analyzing simulations, and experimentally proving signal pathways. Professor Cho has published 140 articles in international journals including Cell, Science, and Nature.
* ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell survival
** ICER (Inducible cAMP early repressor): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell death
*** Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2): Key signal transduction molecule involved in promotion of cell survival
**** β-blocker: Drug that acts as β-adrenergic receptor inhibitor known to slow the progression of heart failure, hence used most commonly in medicine.
Picture: A schematic diagram for the β-AR signalling network
2015.01.05 View 12112
A Key Signal Transduction Pathway Switch in Cardiomyocyte Identified
A KAIST research team has identified the fundamental principle in deciding the fate of cardiomyocyte or heart muscle cells. They have determined that it depends on the degree of stimulus in β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway in the cardiomyocyte to control cells' survival or death. The findings, the team hopes, can be used to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.
The research was led by KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Chair Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and conducted by Dr. Sung-Young Shin (lead author) and Ph.D. candidates Ho-Sung Lee and Joon-Hyuk Kang. The research was conducted jointly with GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology) Department of Biological Sciences Professor Do-Han Kim’s team. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The paper was published in Nature Communications on December 17, 2014 with the title, “The switching role of β-adrenergic receptor signalling in cell survival or death decision of cardiomyocytes.”
The β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway can promote cell survival (mediated by β2 receptors), but also can result in cell death by inducing toxin (mediated by β1 receptors) that leads to various heart diseases including heart failure. Past attempts to identify the fundamental principle in the fate determining process of cardiomyocyte based on β-adrenergic receptor signalling concluded without much success.
The β-adrenergic receptor is a type of protein on the cell membrane of cardiomyocyte (heart muscle cell) that when stimulated by neurohormones such as epinephrine or norepinephrine would transduce signals making the cardiomyocyte contract faster and stronger.
The research team used large-scale computer simulation analysis and systems biology to identify ERK* and ICER** signal transduction pathways mediated by a feed-forward circuit as a key molecular switch that decides between cell survival and death.
Weak β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ERK signal transduction pathway, increasing Bcl-2*** protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte survival. On the other hand, strong β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ICER signal transduction pathway, reducing Bcl-2 protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte death.
Researchers used a systems biology approach to identify the mechanism of B-blocker****, a common drug prescribed for heart failure. When cardiomyocyte is treated with β1 inhibitor, strong stimulation on β-adrenergic receptor increases Bcl-2 expression, improving the chance of cardiomyocyte survival, a cell protection effect.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, “This research used systems biology, an integrated, convergence research of IT (information technology) and BT (biotechnology), to successfully identify the mechanism in deciding the fate of cardiomyocytes based on the β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway for the first time. I am hopeful that this research will enable the control of cardiomyocyte survival and death to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.”
Professor Cho’s team was the first to pioneer a new field of systems biology, especially concerning the complex signal transduction network involved in diseases. Their research is focused on modelling, analyzing simulations, and experimentally proving signal pathways. Professor Cho has published 140 articles in international journals including Cell, Science, and Nature.
* ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell survival
** ICER (Inducible cAMP early repressor): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell death
*** Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2): Key signal transduction molecule involved in promotion of cell survival
**** β-blocker: Drug that acts as β-adrenergic receptor inhibitor known to slow the progression of heart failure, hence used most commonly in medicine.
Picture: A schematic diagram for the β-AR signalling network
2015.01.05 View 12112 -
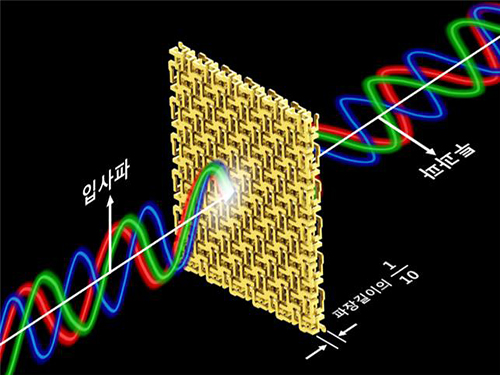 Broadband and Ultrathin Polarization Manipulators Developed
Professor Bumki Min from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST has developed a technology that can manipulate a polarized light in broadband operation with the use of a metamaterial.
It is expected that this technology will lead to the development of broadband optical devices that can be applied to broadband communication and display.
When an object or its structure is analyzed by using a polarized light such as a laser, the results are generally affected by the polarized state of the light. Therefore, in an optics laboratory, the light is polarized by various methods.
In such cases, researchers employ wave plates or photoactive materials. However, the performance of these devices depend vastly on wavelength, and so they are not suitable to be used as a polarizer, especially in broadband.
There were many attempts to make artificial materials that are very photoactive by using metamaterials which have a strong resonance. Nonetheless, because the materials had an unavoidable dispersion in the resonance frequency, they were not adequate for broadband operation.
Professor Min’s research team arranged and connected helical metamaterials that are smaller than the wavelength of light. They verified theoretically and experimentally that polarized light can be constantly rotated regardless of the wavelength by super-thin materials that have thickness less than one-tenth of the wavelength of the light. The experiment which confirmed the theory was conducted in the microwave band.
Broadband polarized rotational 3D metamaterials were found to rotate the polarized microwave within the range of 0.1 GHz to 40 GHz by 45 degrees regardless of its frequency. This nondispersive property is quite unnatural because it is difficult to find a material that does not change in a wide band.
In addition, the research team materialized the broadband nondispersive polarized rotational property by designing the metamaterial in a way that it has chirality, which determines the number of rotations proportional to the wavelength.
Professor Min said, “As the technology is able to manipulate ultrathin polarization of light in broadband, it will lead to the creation of ultra-shallow broadband optical devices.”
Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea, this research was led by a PhD candidate, Hyun-Sung Park, under the guidance of Professor Min. The research findings were published online in the November 17th issue of Nature Communications.
Figure 1 – Broadband and Ultrathin Polarization Manipulators Produced by 3D Printer
Figure 2 – Concept of Broadband and Ultrathin Polarization Manipulators
2014.12.03 View 10355
Broadband and Ultrathin Polarization Manipulators Developed
Professor Bumki Min from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST has developed a technology that can manipulate a polarized light in broadband operation with the use of a metamaterial.
It is expected that this technology will lead to the development of broadband optical devices that can be applied to broadband communication and display.
When an object or its structure is analyzed by using a polarized light such as a laser, the results are generally affected by the polarized state of the light. Therefore, in an optics laboratory, the light is polarized by various methods.
In such cases, researchers employ wave plates or photoactive materials. However, the performance of these devices depend vastly on wavelength, and so they are not suitable to be used as a polarizer, especially in broadband.
There were many attempts to make artificial materials that are very photoactive by using metamaterials which have a strong resonance. Nonetheless, because the materials had an unavoidable dispersion in the resonance frequency, they were not adequate for broadband operation.
Professor Min’s research team arranged and connected helical metamaterials that are smaller than the wavelength of light. They verified theoretically and experimentally that polarized light can be constantly rotated regardless of the wavelength by super-thin materials that have thickness less than one-tenth of the wavelength of the light. The experiment which confirmed the theory was conducted in the microwave band.
Broadband polarized rotational 3D metamaterials were found to rotate the polarized microwave within the range of 0.1 GHz to 40 GHz by 45 degrees regardless of its frequency. This nondispersive property is quite unnatural because it is difficult to find a material that does not change in a wide band.
In addition, the research team materialized the broadband nondispersive polarized rotational property by designing the metamaterial in a way that it has chirality, which determines the number of rotations proportional to the wavelength.
Professor Min said, “As the technology is able to manipulate ultrathin polarization of light in broadband, it will lead to the creation of ultra-shallow broadband optical devices.”
Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea, this research was led by a PhD candidate, Hyun-Sung Park, under the guidance of Professor Min. The research findings were published online in the November 17th issue of Nature Communications.
Figure 1 – Broadband and Ultrathin Polarization Manipulators Produced by 3D Printer
Figure 2 – Concept of Broadband and Ultrathin Polarization Manipulators
2014.12.03 View 10355 -
 Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 10818
Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 10818