Campus/People
-
 Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Opens
The World Economic Forum’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution opened its Korean affiliate center at KAIST on December 10. The Korea Policy Center for the 4th Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will develop policy norms and frameworks for accelerating the benefits of emerging technologies.
Many dignitaries including KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, National Assemblyman Sang-Min Lee, Daejeon City Mayor Her Tae-Jeong, and Managing Director of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Murat Sonmez attended the opening ceremony.
The center will play a vital role in helping to shape the development of national Fourth Industrial Revolution strategies and public-private initiatives. The Center will actively engage with the government on policy design and piloting activities.
The Center is the result of KAIST’s close partnership with the WEF and its Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in San Francisco. KAIST signed an MOU with the WEF in 2017 for this collaboration. Dr. Klaus Schwab expressed his high hopes many times regarding Korea’s potential in responding to the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In addition, he said that KAIST and the City of Daejeon would play a significant role in helping the Fourth Industrial Revolution move forward.
During a meeting with President Moon Jae-In last June, Dr. Schwab expressed his strong desire to collaborate with Korea, and the Korean government designated KAIST as an affiliate center of the WEF.
The KPC4IR had already begun conducting policy research in the areas of block chain and precision medicine even before making a partnership with the WEF. The director of the Center, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, said, “We have focused on the development of technology but rarely talk about governance. Technology should come with policy. We will conduct policy development on how to ensure inclusive growth capitalizing on emerging technologies. We will also make policy guidelines for technological applications after considering all the ethical perspectives.
President Shin also said in his opening remarks, “Korea has been a fast follower over the past decades in making economic development and innovations. I believe that the Fourth Industrial Revolution gives us the best opportunity to play the role of ‘first mover.’ I look forward to the KPC4IR serving as a ‘Think and Do’ tank, not limiting itself to the role of ‘think tank.’ We will continue to work closely with the WEF in the fields of AI, blockchain, and precision medicine.
2019.12.10 View 7177
Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Opens
The World Economic Forum’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution opened its Korean affiliate center at KAIST on December 10. The Korea Policy Center for the 4th Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will develop policy norms and frameworks for accelerating the benefits of emerging technologies.
Many dignitaries including KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, National Assemblyman Sang-Min Lee, Daejeon City Mayor Her Tae-Jeong, and Managing Director of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Murat Sonmez attended the opening ceremony.
The center will play a vital role in helping to shape the development of national Fourth Industrial Revolution strategies and public-private initiatives. The Center will actively engage with the government on policy design and piloting activities.
The Center is the result of KAIST’s close partnership with the WEF and its Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in San Francisco. KAIST signed an MOU with the WEF in 2017 for this collaboration. Dr. Klaus Schwab expressed his high hopes many times regarding Korea’s potential in responding to the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In addition, he said that KAIST and the City of Daejeon would play a significant role in helping the Fourth Industrial Revolution move forward.
During a meeting with President Moon Jae-In last June, Dr. Schwab expressed his strong desire to collaborate with Korea, and the Korean government designated KAIST as an affiliate center of the WEF.
The KPC4IR had already begun conducting policy research in the areas of block chain and precision medicine even before making a partnership with the WEF. The director of the Center, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, said, “We have focused on the development of technology but rarely talk about governance. Technology should come with policy. We will conduct policy development on how to ensure inclusive growth capitalizing on emerging technologies. We will also make policy guidelines for technological applications after considering all the ethical perspectives.
President Shin also said in his opening remarks, “Korea has been a fast follower over the past decades in making economic development and innovations. I believe that the Fourth Industrial Revolution gives us the best opportunity to play the role of ‘first mover.’ I look forward to the KPC4IR serving as a ‘Think and Do’ tank, not limiting itself to the role of ‘think tank.’ We will continue to work closely with the WEF in the fields of AI, blockchain, and precision medicine.
2019.12.10 View 7177 -
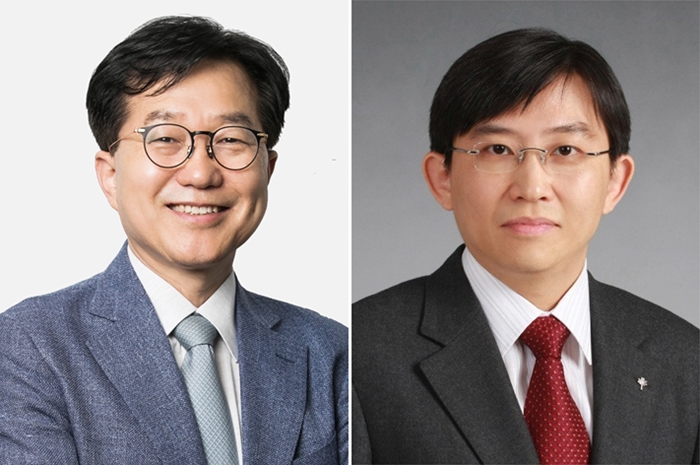 New Members of KAST 2020
< Professor Zong-Tae Bae (Left) and Professor Sang Ouk Kim (Right) >
Professor Zong-Tae Bae from the School of Management Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering became new fellows of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) along with 22 other scientists in Korea.
On November 22, KAST announced 24 new members for the year 2020. This includes seven scientists from the field of natural sciences, six from engineering, four from medical sciences, another four from policy research, and three from agriculture and fishery.
The new fellows will begin their term from January next year, and their fellowships wll be conferred during the KAST’s New Year Reception to be held on January 14 in Seoul.
(END)
2019.12.09 View 10212
New Members of KAST 2020
< Professor Zong-Tae Bae (Left) and Professor Sang Ouk Kim (Right) >
Professor Zong-Tae Bae from the School of Management Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering became new fellows of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) along with 22 other scientists in Korea.
On November 22, KAST announced 24 new members for the year 2020. This includes seven scientists from the field of natural sciences, six from engineering, four from medical sciences, another four from policy research, and three from agriculture and fishery.
The new fellows will begin their term from January next year, and their fellowships wll be conferred during the KAST’s New Year Reception to be held on January 14 in Seoul.
(END)
2019.12.09 View 10212 -
 KAIST Awarded the IPBC R&D Institution Team of the Year
KAIST was awarded the R&D Institution Team of the Year during the annual IPBC (Intellectual Property Business Congress) Asia 2019 held in Tokyo October 28-30. IPBC is a conference dedicated to IP value creation strategies hosted by IAM Media, a world’s leading IP business media platform.
IPBC Asia 2019 recognized the institutions and businesses that employed innovative IP strategies and management to produce the greatest IP value in 11 categories covering automotive, electronics, healthcare and biotechnology, internet and software, R&D institutions, semiconductors, industrials, mobile and telecommunications, Asia IP deals, Asia teams, and Asia individuals. This year, KAIST was recognized as one of the most active patentees in the Asia-Pacific region by significantly increasing its IP value through licensing and tech transfers.
Associate Vice President Kyung Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation remarked, “We are so delighted to prove the strong research capacity of KAIST. This will help us accomplish our vision of being a leading university that creates global impact.”
2019.12.04 View 6411
KAIST Awarded the IPBC R&D Institution Team of the Year
KAIST was awarded the R&D Institution Team of the Year during the annual IPBC (Intellectual Property Business Congress) Asia 2019 held in Tokyo October 28-30. IPBC is a conference dedicated to IP value creation strategies hosted by IAM Media, a world’s leading IP business media platform.
IPBC Asia 2019 recognized the institutions and businesses that employed innovative IP strategies and management to produce the greatest IP value in 11 categories covering automotive, electronics, healthcare and biotechnology, internet and software, R&D institutions, semiconductors, industrials, mobile and telecommunications, Asia IP deals, Asia teams, and Asia individuals. This year, KAIST was recognized as one of the most active patentees in the Asia-Pacific region by significantly increasing its IP value through licensing and tech transfers.
Associate Vice President Kyung Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation remarked, “We are so delighted to prove the strong research capacity of KAIST. This will help us accomplish our vision of being a leading university that creates global impact.”
2019.12.04 View 6411 -
 KAIST and Google Jointly Develop AI Curricula
KAIST selected the two professors who will develop AI curriculum under the auspices of the KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research. The Graduate School of AI announced the two authors among the 20 applicants who will develop the curriculum next year. They will be provided 7,500 USD per subject.
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Yong-Jin Yoon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will use Google technology such as TensorFlow, Google Cloud, and Android to create the curriculum.
Professor Suh’s “TensorFlow for Information Theory and Convex Optimization “will be used for curriculum in the graduate courses and Professor Yoon’s “AI Convergence Project Based Learning (PBL)” will be used for online courses. Professor Yoon’s course will explore and define problems by utilizing AI and experiencing the process of developing products that use AI through design thinking, which involves product design, production, and verification. Professor Suh’s course will discus“information theory and convergence,” which uses basic sciences and engineering as well as AI, machine learning, and deep learning.
2019.12.04 View 11025
KAIST and Google Jointly Develop AI Curricula
KAIST selected the two professors who will develop AI curriculum under the auspices of the KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research. The Graduate School of AI announced the two authors among the 20 applicants who will develop the curriculum next year. They will be provided 7,500 USD per subject.
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Yong-Jin Yoon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will use Google technology such as TensorFlow, Google Cloud, and Android to create the curriculum.
Professor Suh’s “TensorFlow for Information Theory and Convex Optimization “will be used for curriculum in the graduate courses and Professor Yoon’s “AI Convergence Project Based Learning (PBL)” will be used for online courses. Professor Yoon’s course will explore and define problems by utilizing AI and experiencing the process of developing products that use AI through design thinking, which involves product design, production, and verification. Professor Suh’s course will discus“information theory and convergence,” which uses basic sciences and engineering as well as AI, machine learning, and deep learning.
2019.12.04 View 11025 -
 KAIST Alumnus NYU Professor Supports Female AI Researchers
A KAIST alumnus and an associate professor at New York University (NYU), Dr. Kyunghyun Cho donated 3,000 USD to the KAIST Graduate School of AI to support female AI researchers.
Professor Cho spoke as a guest lecturer at the 2019 Samsung AI Forum on November 4 and received 3,000 USD as an honorarium. He donated this honorarium to the KAIST Graduate School of AI with a special request to support the school’s female PhD students attending the 2020 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), where he serves as a program co-chair.
Professor Cho received his BS degree from KAIST’s School of Computing in 2009 and is now serving as an associate professor at NYU’s Computer Science Department and Center for Data Science. His research mainly covers machine learning and natural language processing.
Professor Cho said that he decided to make this donation because “In Korea and even in the US, women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) lack opportunities and environments that allow them to excel.”
Professor Song Chong, the Head of the KAIST Graduate School of AI, responded, “We are so grateful for Professor Kyunghyun Cho’s contribution and we will also use funds from the school in addition to the donation to support our female PhD students who will attend the ICLR.”
(END)
2019.11.15 View 7084
KAIST Alumnus NYU Professor Supports Female AI Researchers
A KAIST alumnus and an associate professor at New York University (NYU), Dr. Kyunghyun Cho donated 3,000 USD to the KAIST Graduate School of AI to support female AI researchers.
Professor Cho spoke as a guest lecturer at the 2019 Samsung AI Forum on November 4 and received 3,000 USD as an honorarium. He donated this honorarium to the KAIST Graduate School of AI with a special request to support the school’s female PhD students attending the 2020 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), where he serves as a program co-chair.
Professor Cho received his BS degree from KAIST’s School of Computing in 2009 and is now serving as an associate professor at NYU’s Computer Science Department and Center for Data Science. His research mainly covers machine learning and natural language processing.
Professor Cho said that he decided to make this donation because “In Korea and even in the US, women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) lack opportunities and environments that allow them to excel.”
Professor Song Chong, the Head of the KAIST Graduate School of AI, responded, “We are so grateful for Professor Kyunghyun Cho’s contribution and we will also use funds from the school in addition to the donation to support our female PhD students who will attend the ICLR.”
(END)
2019.11.15 View 7084 -
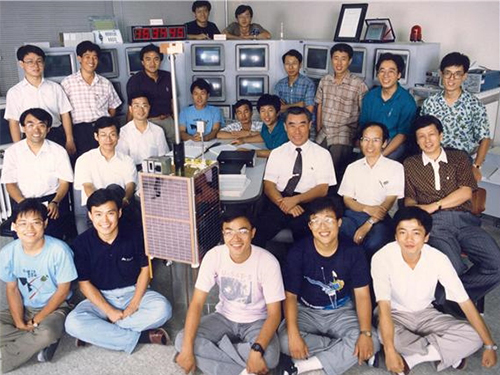 SaTReC, Birthplace of Korea’s First Satellite, Celebrates 30th Anniversary
< SaTReC researchers who developed Korea's first satellite, KITSAT-1 >
The Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, which launched the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1, celebrated 30 years in operation last week. A ceremony in honor of this milestone was held on campus on October 30. With the launching of KITSAT-1 in 1992, SaTReC paved the way for space research in Korea, and helped the nation achieve technological independence and strengthen competitiveness in the field.
The ceremony was attended by over 100 affiliates from academia and industry, including the family of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, the first director of SaTReC also known as the father of the first Korean satellite KITSAT-1 (nicknamed “Our Star” in Korean). His family members traveled all the way from the US to Korea for the event. A plaque of appreciation was posthumously awarded to the family of former Director Choi in memory of his pioneering Korean satellite research.
Right after the establishment of SaTReC in 1989, Dr.Choi dispatched five KAIST students to the University of Surrey in the UK to develop the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1 under a bilateral agreement for a joint research program.
KITSAT-1, completed in collaboration with Surrey researchers, was successfully launched from the Guiana Space Center in August 1992. Through this launch, Korea became the 22nd nation to own a satellite, and launched the domestically produced follow-up satellite KITSAT-2 in September 1993.
Since then, SaTReC has developed a total of nine satellites, including three in the KITSAT series in the 1990s as well as five STSATs and one Next-Generation Small Satellite in the 2000s. These satellites are still in operation today, thanks to SaTReC’s constant maintenance.
SaTReC is still contributing to the verification of core space technologies and Earth and space observation technologies using small satellites. It is also training specialized personnel in national space research and development.
Most significantly, STSAT-2C, also commonly known as the Naro Science Satellite, was launched on January 30, 2013 and served an important role in allowing the first Korean launch vehicle Naro-1 (KSLV-1) to enter into orbit.
SaTReC researchers are now working on developing a Next-Generation Small Satellite named NEXTSat-2 that boasts a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system developed with domestic technology. NEXTSat-2 will be launched in 2022 from Korean soil, carried by a Korean launch vehicle developed with local technology.
Director of SaTReC Sejin Kwon said, “We will follow the noble spirit of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, who dedicated his entire life to the nation’s satellite research and bolstered our commitment to the development of Korea’s future space technology.” He added, “We will pursue our dreams of space exploration with a sense of social responsibility to pay back to society the benefits reaped from space technology.”
The ceremony was followed by a Future Space Technology Workshop, where eight KAIST professors participated as speakers.
< Timeline of Korea's Satellite Research and Development >
(END)
2019.11.05 View 5699
SaTReC, Birthplace of Korea’s First Satellite, Celebrates 30th Anniversary
< SaTReC researchers who developed Korea's first satellite, KITSAT-1 >
The Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, which launched the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1, celebrated 30 years in operation last week. A ceremony in honor of this milestone was held on campus on October 30. With the launching of KITSAT-1 in 1992, SaTReC paved the way for space research in Korea, and helped the nation achieve technological independence and strengthen competitiveness in the field.
The ceremony was attended by over 100 affiliates from academia and industry, including the family of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, the first director of SaTReC also known as the father of the first Korean satellite KITSAT-1 (nicknamed “Our Star” in Korean). His family members traveled all the way from the US to Korea for the event. A plaque of appreciation was posthumously awarded to the family of former Director Choi in memory of his pioneering Korean satellite research.
Right after the establishment of SaTReC in 1989, Dr.Choi dispatched five KAIST students to the University of Surrey in the UK to develop the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1 under a bilateral agreement for a joint research program.
KITSAT-1, completed in collaboration with Surrey researchers, was successfully launched from the Guiana Space Center in August 1992. Through this launch, Korea became the 22nd nation to own a satellite, and launched the domestically produced follow-up satellite KITSAT-2 in September 1993.
Since then, SaTReC has developed a total of nine satellites, including three in the KITSAT series in the 1990s as well as five STSATs and one Next-Generation Small Satellite in the 2000s. These satellites are still in operation today, thanks to SaTReC’s constant maintenance.
SaTReC is still contributing to the verification of core space technologies and Earth and space observation technologies using small satellites. It is also training specialized personnel in national space research and development.
Most significantly, STSAT-2C, also commonly known as the Naro Science Satellite, was launched on January 30, 2013 and served an important role in allowing the first Korean launch vehicle Naro-1 (KSLV-1) to enter into orbit.
SaTReC researchers are now working on developing a Next-Generation Small Satellite named NEXTSat-2 that boasts a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system developed with domestic technology. NEXTSat-2 will be launched in 2022 from Korean soil, carried by a Korean launch vehicle developed with local technology.
Director of SaTReC Sejin Kwon said, “We will follow the noble spirit of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, who dedicated his entire life to the nation’s satellite research and bolstered our commitment to the development of Korea’s future space technology.” He added, “We will pursue our dreams of space exploration with a sense of social responsibility to pay back to society the benefits reaped from space technology.”
The ceremony was followed by a Future Space Technology Workshop, where eight KAIST professors participated as speakers.
< Timeline of Korea's Satellite Research and Development >
(END)
2019.11.05 View 5699 -
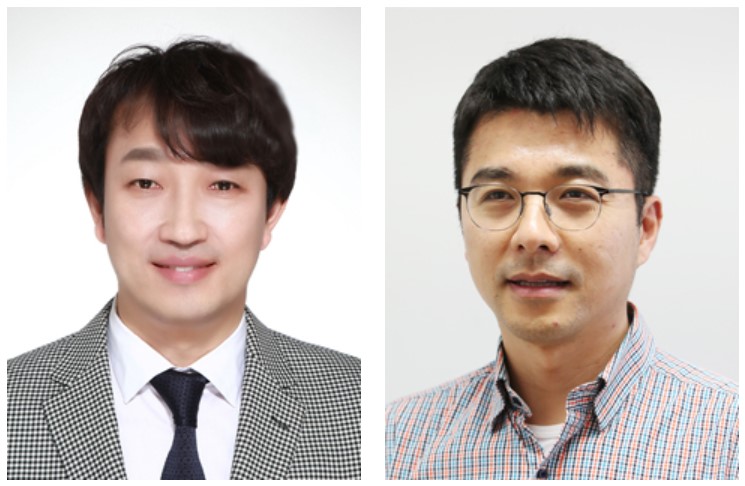 Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 9200
Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 9200 -
 Professor Byong-Guk Park Named Scientist of October
< Professor Byong-Guk Park >
Professor Byong-Guk Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2019 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Park was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of spin-orbit torque (SOT)-based magnetic random access memory (MRAM) technology. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
A next-generation, non-volatile memory device MRAM consists of thin magnetic films. It can be applied in “logic-in-memory” devices, in which logic and memory functionalities coexist, thus drastically improving the performance of complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) processors. Conventional MRAM technology is limited in its ability to increase the operation speed of a memory device while maintaining a high density.
Professor Park tackled this challenge by introducing a new material, antiferromagnet (IrMn), that generates a sizable amount of SOT as well as an exchange-bias field, which makes successful data writing possible without an external magnetic field. This research outcome paved the way for the development of MRAM, which has a simple device structure but features high speeds and density.
Professor Park said, “I feel rewarded to have forwarded the feasibility and applicability of MRAM. I will continue devoting myself to studying further on the development of new materials that can help enhance the performance of memory devices."
(END)
2019.10.10 View 7993
Professor Byong-Guk Park Named Scientist of October
< Professor Byong-Guk Park >
Professor Byong-Guk Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2019 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Park was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of spin-orbit torque (SOT)-based magnetic random access memory (MRAM) technology. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
A next-generation, non-volatile memory device MRAM consists of thin magnetic films. It can be applied in “logic-in-memory” devices, in which logic and memory functionalities coexist, thus drastically improving the performance of complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) processors. Conventional MRAM technology is limited in its ability to increase the operation speed of a memory device while maintaining a high density.
Professor Park tackled this challenge by introducing a new material, antiferromagnet (IrMn), that generates a sizable amount of SOT as well as an exchange-bias field, which makes successful data writing possible without an external magnetic field. This research outcome paved the way for the development of MRAM, which has a simple device structure but features high speeds and density.
Professor Park said, “I feel rewarded to have forwarded the feasibility and applicability of MRAM. I will continue devoting myself to studying further on the development of new materials that can help enhance the performance of memory devices."
(END)
2019.10.10 View 7993 -
 Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 5636
Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 5636 -
 Professor Ki-Jun Yoon selected as the 2019 SUHF Young Investigator
< Professor Ki-Jun Yoon >
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of four recipients of the 2019 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Awards.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year, and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 83 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the four recipients, including Professor Yoon.
Professor Yoon was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of research on how post-transcriptional mechanisms may modulate stem cell properties. His research project involves deciphering the molecular mechanisms controlling RNA metabolism in neural stem cells during normal development, and how alterations in RNA regulatory programs lead to human brain disorders.
< (From left) Professor Joo-Hong Park, Professor Yuree Lee, Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh, Professor Eunjung Lee, Professor Ki-Jun Yoon, ⓒ Amorepacific Group >
The other awards were given to Professor Joo-Hong Park and Professor Yuree Lee of Seoul National University, and Professor Eunjung Lee of Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The awards ceremony was held on September 18 at the Amorepacific Headquarters in Seoul.
With these four new awardees, a total of 14 scientists have been named as SUHF Young Investigators to date.
(END)
2019.09.23 View 7414
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon selected as the 2019 SUHF Young Investigator
< Professor Ki-Jun Yoon >
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of four recipients of the 2019 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Awards.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year, and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 83 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the four recipients, including Professor Yoon.
Professor Yoon was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of research on how post-transcriptional mechanisms may modulate stem cell properties. His research project involves deciphering the molecular mechanisms controlling RNA metabolism in neural stem cells during normal development, and how alterations in RNA regulatory programs lead to human brain disorders.
< (From left) Professor Joo-Hong Park, Professor Yuree Lee, Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh, Professor Eunjung Lee, Professor Ki-Jun Yoon, ⓒ Amorepacific Group >
The other awards were given to Professor Joo-Hong Park and Professor Yuree Lee of Seoul National University, and Professor Eunjung Lee of Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The awards ceremony was held on September 18 at the Amorepacific Headquarters in Seoul.
With these four new awardees, a total of 14 scientists have been named as SUHF Young Investigators to date.
(END)
2019.09.23 View 7414 -
 KAIST to Transfer Core Tech to Domestic Companies amid Japan's Export Curbs
< Associate Vice President Kyung-Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) at KAIST >
KAIST will transfer four core technologies related to materials, parts, and equipment to domestic companies to help them combat the latest export curbs triggered by Korea’s removal from Japan’s ‘white list’ of preferential trade partners. In addition, KAIST’s five patented technologies in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and materials and parts will also be transferred to the companies in order to reduce the reliance on Japan and achieve technological independence through the ‘localization’ of key technologies.
KAIST announced these university-industry cooperation promotion plans at the ‘2019 KAIST Core Tech Transfer Day Conference’ held in Seoul on September 17. More than 200 entrepreneurs and investors attended the briefing and on-site consulting sessions delivered by nine KAIST professors who led the development of the technologies.
The four technologies were presented at the conference as those that can replace Japanese technologies subject to the export curbs. They include:
1. ‘Transparent fluorinated polyimide with low thermal expansion’ developed by Professor Sang-Youl Kim of the Department of Chemistry
2. ‘A non-destructive electromagnetic performance testing system’ developed by Professor Jung-Ryul Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering
3. ‘A nanotechnology-based electrode material for use in advanced secondary batteries’ developed by Professor Do-Kyung Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
4. ‘A high-resolution photoresist’ developed by Professor Emeritus Jin-Baek Kim of the Department of Chemistry.
Of particular interest is the non-destructive electromagnetic performance testing system technology developed by Professor Jung-Ryul Lee. This new cost-effective technology enables tests that were impossible to carry out using conventional technologies and yields a cost reduction of more than 50 percent compared to foreign technologies.
By introducing Professor Do-Kyung Kim’s new electrode material technology, the efficiency of electric vehicles can be increased. As this technology uses relatively low-cost sodium ion batteries, industries can prepare for the possible jump from the more expensive lithium batteries currently being used.
Another five patented AI and materials and parts technologies disclosed at the conference include:
1. ‘Enhanced HTTP adaptive streaming with CNN-based super-resolution’ developed by Professor Dong-soo Han of the School of Electrical Engineering
2. ‘Method and apparatus of brain-computer interface design for estimating choice behavior and decision strategy’ developed by Professor Sang-Wan Lee of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
3. ‘Eco-friendly fabrication of metal oxide nanoparticles and fabrication of non-toxic polymer sunscreen ingredients by electron irradiation’ developed by Professor Sung-Oh Cho of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering
4. ‘High-density nanofiber yarn-based coloricmetric gas sensors’ developed by Professor Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
5. ‘Silicon-pocket energy storage electrode with high energy density and its manufacturing technology’ developed by Professor Jeung-Ku Kang of the Graduate school of EEWS.
The patented nanofiber-based coloricmetric gas sensor technology developed by Professor Il-Doo Kim allows for the diagnosis of diseases by only using the patient’s respiration. Due to its high productivity and processability, it is expected to be applied to various fields in the fast-growing disease diagnosis sensor market, which includes mobile devices and wearable sensors.
Moreover, Professor Dong-soo Han’s patented adaptive streaming technology attracted attention along with the ever-growing Over The Top (OTT) and Video On Demand (VOD) service markets, since it has significant potential for improving the streaming quality of videos and reducing costs for video providers.
Professor Kyung-Cheol Choi, the Associate Vice President of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) at KAIST, said, “KAIST OUIC and KAIST Advisors on Materials and Parts (KAMP) have been working tirelessly to help Korean companies cope with the recent Japanese export restrictions. KAIST’s efforts will enhance the competitiveness and growth of the Korean industry and economy, turning this national crisis into opportunity.”
(END)
2019.09.20 View 5787
KAIST to Transfer Core Tech to Domestic Companies amid Japan's Export Curbs
< Associate Vice President Kyung-Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) at KAIST >
KAIST will transfer four core technologies related to materials, parts, and equipment to domestic companies to help them combat the latest export curbs triggered by Korea’s removal from Japan’s ‘white list’ of preferential trade partners. In addition, KAIST’s five patented technologies in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and materials and parts will also be transferred to the companies in order to reduce the reliance on Japan and achieve technological independence through the ‘localization’ of key technologies.
KAIST announced these university-industry cooperation promotion plans at the ‘2019 KAIST Core Tech Transfer Day Conference’ held in Seoul on September 17. More than 200 entrepreneurs and investors attended the briefing and on-site consulting sessions delivered by nine KAIST professors who led the development of the technologies.
The four technologies were presented at the conference as those that can replace Japanese technologies subject to the export curbs. They include:
1. ‘Transparent fluorinated polyimide with low thermal expansion’ developed by Professor Sang-Youl Kim of the Department of Chemistry
2. ‘A non-destructive electromagnetic performance testing system’ developed by Professor Jung-Ryul Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering
3. ‘A nanotechnology-based electrode material for use in advanced secondary batteries’ developed by Professor Do-Kyung Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
4. ‘A high-resolution photoresist’ developed by Professor Emeritus Jin-Baek Kim of the Department of Chemistry.
Of particular interest is the non-destructive electromagnetic performance testing system technology developed by Professor Jung-Ryul Lee. This new cost-effective technology enables tests that were impossible to carry out using conventional technologies and yields a cost reduction of more than 50 percent compared to foreign technologies.
By introducing Professor Do-Kyung Kim’s new electrode material technology, the efficiency of electric vehicles can be increased. As this technology uses relatively low-cost sodium ion batteries, industries can prepare for the possible jump from the more expensive lithium batteries currently being used.
Another five patented AI and materials and parts technologies disclosed at the conference include:
1. ‘Enhanced HTTP adaptive streaming with CNN-based super-resolution’ developed by Professor Dong-soo Han of the School of Electrical Engineering
2. ‘Method and apparatus of brain-computer interface design for estimating choice behavior and decision strategy’ developed by Professor Sang-Wan Lee of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
3. ‘Eco-friendly fabrication of metal oxide nanoparticles and fabrication of non-toxic polymer sunscreen ingredients by electron irradiation’ developed by Professor Sung-Oh Cho of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering
4. ‘High-density nanofiber yarn-based coloricmetric gas sensors’ developed by Professor Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
5. ‘Silicon-pocket energy storage electrode with high energy density and its manufacturing technology’ developed by Professor Jeung-Ku Kang of the Graduate school of EEWS.
The patented nanofiber-based coloricmetric gas sensor technology developed by Professor Il-Doo Kim allows for the diagnosis of diseases by only using the patient’s respiration. Due to its high productivity and processability, it is expected to be applied to various fields in the fast-growing disease diagnosis sensor market, which includes mobile devices and wearable sensors.
Moreover, Professor Dong-soo Han’s patented adaptive streaming technology attracted attention along with the ever-growing Over The Top (OTT) and Video On Demand (VOD) service markets, since it has significant potential for improving the streaming quality of videos and reducing costs for video providers.
Professor Kyung-Cheol Choi, the Associate Vice President of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) at KAIST, said, “KAIST OUIC and KAIST Advisors on Materials and Parts (KAMP) have been working tirelessly to help Korean companies cope with the recent Japanese export restrictions. KAIST’s efforts will enhance the competitiveness and growth of the Korean industry and economy, turning this national crisis into opportunity.”
(END)
2019.09.20 View 5787 -
 School of Transdisciplinary Studies Aims to Attract New Talents
KAIST opened the School of Transdisciplinary Studies to foster ‘convergent talents’ who can create new knowledge through a transdisciplinary approach. The new department will officially start classes in the spring semester of 2020 while recruiting its first cohorts during the fall semester among current freshmen.
President Sung-Chul Shin, the Head of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies Jong Duk Kim, and other prominent members of KAIST’s administration celebrated the opening of the new department during a ceremony on September 18. Students who will declare their major this semester and many parents showed strong interests in this new department while attending the ceremony. They all toured the new facilities together and attended the special lecture sessions.
The School of Transdisciplinary Studies is designed to empower students to create new solutions to emerging complex technologies and rapidly evolving global issues. This is one of the education innovation initiatives under Vision 2031, the plan President Sung-Chul Shin has launched to nurture creative young convergent leaders, and the first single transdisciplinary department that will be introduced in a Korean university.
The new faculty aims to educate students who will have a deeper understanding of the humanities, scientific creativity, the ability to conceive new ideas, complex problem-solving skills, and global leadership. The curriculum boasts a strong foundation of basic science and humanities over six required courses in physics, chemistry, molecular biology, applied mathematics modeling, data structure, and economics. Then, students will explore their academic depth by choosing one of eight emerging fields. The eight concentration majors encompass data and AI, smart cities and media, healthcare, culture and media, management and startups, materials and matter, energy and environment, and machinery and precision. In their third and fourth years, students can customize their study course based on their career path and academic interest after consultation with a faculty mentor and an internship. Upon graduation, they will earn a bachelor’s degree in convergent science or a bachelor of convergent engineering degree. They may also elect to receive a bachelor’s degree in science or engineering.
“This faculty offers deep knowledge in basic science and humanities to help students explore their specialties more creatively. Specialties built upon strong theory and creative applicability will be the key to solving the global challenges in an era of volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity,” said Professor Kim, the head of the school, at the ceremony.
President Shin also stressed the importance of convergence education during his special lecture, saying, “We will continue to strive to foster new talents who will create new convergent knowledge in emerging technologies such as IoT, big data, 5G, and AI. By fostering such young convergent talents, we will take the lead in national development and work for the prosperity of humanity.”
(END)
2019.09.19 View 4867
School of Transdisciplinary Studies Aims to Attract New Talents
KAIST opened the School of Transdisciplinary Studies to foster ‘convergent talents’ who can create new knowledge through a transdisciplinary approach. The new department will officially start classes in the spring semester of 2020 while recruiting its first cohorts during the fall semester among current freshmen.
President Sung-Chul Shin, the Head of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies Jong Duk Kim, and other prominent members of KAIST’s administration celebrated the opening of the new department during a ceremony on September 18. Students who will declare their major this semester and many parents showed strong interests in this new department while attending the ceremony. They all toured the new facilities together and attended the special lecture sessions.
The School of Transdisciplinary Studies is designed to empower students to create new solutions to emerging complex technologies and rapidly evolving global issues. This is one of the education innovation initiatives under Vision 2031, the plan President Sung-Chul Shin has launched to nurture creative young convergent leaders, and the first single transdisciplinary department that will be introduced in a Korean university.
The new faculty aims to educate students who will have a deeper understanding of the humanities, scientific creativity, the ability to conceive new ideas, complex problem-solving skills, and global leadership. The curriculum boasts a strong foundation of basic science and humanities over six required courses in physics, chemistry, molecular biology, applied mathematics modeling, data structure, and economics. Then, students will explore their academic depth by choosing one of eight emerging fields. The eight concentration majors encompass data and AI, smart cities and media, healthcare, culture and media, management and startups, materials and matter, energy and environment, and machinery and precision. In their third and fourth years, students can customize their study course based on their career path and academic interest after consultation with a faculty mentor and an internship. Upon graduation, they will earn a bachelor’s degree in convergent science or a bachelor of convergent engineering degree. They may also elect to receive a bachelor’s degree in science or engineering.
“This faculty offers deep knowledge in basic science and humanities to help students explore their specialties more creatively. Specialties built upon strong theory and creative applicability will be the key to solving the global challenges in an era of volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity,” said Professor Kim, the head of the school, at the ceremony.
President Shin also stressed the importance of convergence education during his special lecture, saying, “We will continue to strive to foster new talents who will create new convergent knowledge in emerging technologies such as IoT, big data, 5G, and AI. By fostering such young convergent talents, we will take the lead in national development and work for the prosperity of humanity.”
(END)
2019.09.19 View 4867