research

< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
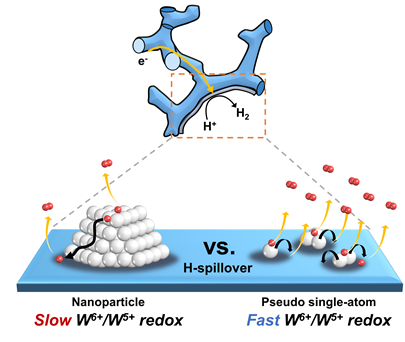
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-Profile
Professor Jinwoo Lee
Convergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratory
http://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
- No Data